
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you want to know electrical resistors and their importance in electronics? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and Learn Everything From Scratch!
electrical resistors are also known as electronic components which are used in circuits to vary current and voltage values. All these terms are widely used in electronics, since they must be used when wanting to carry out any type of electrical project such as Arduino projects.
By working with a platform like Arduino it is more than necessary that the user has some prior knowledge of electronics and electronic components, since all this will be fundamental for what development is in the platform and the programming of each one of the plates, especially since each type of device requires a proper voltage supply.
This means that a bad handling of the resistances that are handled in the circuits could cause a irreparable damage to one of the Arduino boards by not working with the necessary knowledge. That is why here we are going to teach you a little more about what it is the electrical resistance, what it is for and what are all the types that currently existfor this follow everything that we will teach you next in the post.
What is electrical resistance and what is it used for in electronics?
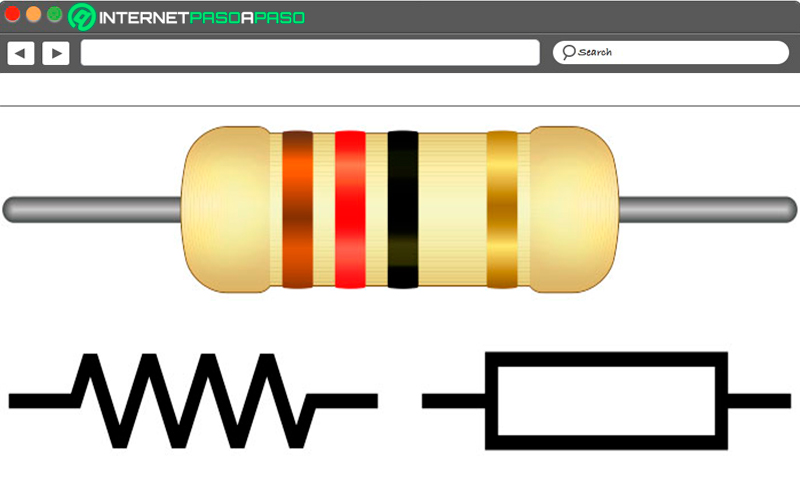
electrical resistance is defined as the opposition that an element has before the passage of the current or in such a case it can also be defined as the force that repels or opposes moving electrons in the material. The more the circuit element opposes the flow of current, the more resistance will be generated.
Different methods are used for its measurement, the most common and used today are ohmmeter or multimeterit is a device that is placed at the tip of each terminal, in this way you can obtain the value of electrical resistance that is being generated there.
Therefore, it can be said that the function of all this is to help limit and control the voltage of the electrical current, it is measured by the ohms and is represented with the letter R. In the same way all this is also known as electronic components that are used in circuits for a change current and voltage values.
Mostly when working in electronics it is necessary to power a device, but for this you only have one voltage source which can be much larger than the terminal needs, so it can be damaged if it is connected directly. This is something that happens frequently when working with Led lights in Arduino projectssince when connecting them directly to a +5V pin, the current flowing will be too high for the led and this causes it to burn.
In order to avoid this, the correct thing to do is connect the Led to an electrical resistance of 220 ohms or similarthis will make the intensity value much smaller and even though the Led will look a little less bright than if it is connected directly, but this will help extend its useful life, so that element will be taken care of and ensuring the proper functioning of the project.
Behavior of electrical resistance How does this factor work in circuits?
It must be borne in mind that electrical resistance behaves in two ways, one of them is direct current and alternating current.
That is why we are going to explain what it consists of and how each of them works:
in direct current
In the case of direct current, it refers to what is the continuous flow of electric charge through a conductor between two points of different potential, the same does not change direction over time. Here you can also see how the electric charges circulate always in the same direction, although direct current is mostly identified with a constant current.
In this case, all current that always maintains the same current is called continuous. polarity, thus reduce the intensity as the load is consumed. It is also called direct current when electrons always move in the same directionthe flow is called DC and always goes from positive pole to negative pole.
Therefore, it can be said that this type of current is produced by batteries and batterieswhere the terminal ends of any of these Electric generators They create a constant tension that will not vary over time. Usually the meaning of the electric current It is considered that it goes from positive to negative, but the truth of all this is that the direction of the movement of the electrons goes from the negative to positive.
So that you can understand much better what a direct current is, here we leave you the following example:
- having a 15 volt batteryany type of receiver that connects to it will always have 12 volts, being a direct current, the battery voltage will not vary over time. Therefore, connecting a receiver to either a lamp or a radio, the current what is going to circulate through the circuit will always be constant that is, the same number of electrons and it will not vary in direction of circulation, so it will always maintain the same direction, it will go from the positive pole to the negative pole.
Finally it can be said that direct current always has the same voltage the intensity of the current equal and all the current will always flow in the same direction.
in alternating current
In the case of alternating current it is a type of electric current where the direction of electron flow comes and goes in regular intervals or through cycles. Therefore, the current flowing through power lines and the electricity normally available in homes is made through wall sockets which have alternating current. In the case of the United States, the standard current used is 60 cycles per secondwhich means that it has a 60hz frequency.
While in Europe and most of the world the standard current used is 50 cycles per second, that is, they have a 50hz frequency In the same way this type of current is produced by the alternators and is what is generated in power plants. In the case of alternating current this is much easier to generate and transportthat is why it is the most used in the world, since it is mostly the one found in the connectors installed in homes and offices.
To produce it, it is necessary for the alternator to do spin its rotor 50 times every secondwhere thanks to electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction each turn of the alternator is capable of produce a sinusoidal or sinusoidal current and voltage wave. Regarding the rotational speed of the alternator, it is constant, so it can be said that the alternators have a frequency of 50 Hertz (Hz) or what can also be said to give 50 laps per second.
Types of electrical resistors. What are all the ones that exist and how do they differ?
can currently be found three types of electrical resistance.
Which we are going to show you next:
Fixed resistors
Fixed resistors are those that present the same value without the possibility that they can reach be modified at will.
It is divided into the following types:
- Agglomerated: They are those that are built through a mixture of graphite and insulating materials in adequate proportions to obtain the desired ohmic value, it is expressed through the color code. However, it should be mentioned that this type of uses little because it presents a poor accuracy and thermal instability. It has a dissipation power ranging from 1/8W to 2W
- carbon film: This consists of a cylinder of an insulating material on which a thin carbon layer with two caps at the ends. To find its ohmic value is going to get carving a helix along the carbon surface and it is presented by the color code. They are one of the most used for small powers ranging from 1/10 W up to 2 W.
- metallic film: These are built in an identical way to those mentioned above, but this time with a thin metal alloy film that makes them be much more temperature stable. In this way, electrical resistors of this type are very precise. It should also be mentioned that they use five colored rings to be able to represent its value corresponding to the first four ohmic values.
- Windings: Those of this type are constructed by winding wire of an alloy of Ni-Cr-Al over a ceramic tube and then coating it with a layer of enamel. In this case the ohmic value is indicated on the surface and are manufactured up to values of 220 k Y dissipation powers range from 1W to 130.
Variable resistor
Variable resistor is also known as potentiometer and it allows you to modify your ohmic value from zero to a maximum value via a scrollable element or cursor.
It has the following types:
- Windings: They are also known as rheostats or potentiometersthis will depend on the power that these are capable of dissipating, they are made up of a ceramic body that normally has the shape of a bull, on which a metallic thread note or an alloy Ni-Cr-Al covered with a vitrified enamel along the entire surface, except for a side track through which a metal slider can slide. In the case of rheostats, they are used in high-consumption circuits.
- carbon film: They are made up of a sheet of agglomerated carbon deposited on a circular insulating base or rectilinear with two terminals at both ends on which a mobile contact or cursorall this is attached to a third connection terminal.
In this way you can get the value you want between any of the ends and the cursor. Depending on the type of variation, one can speak of linear and logarithmic potentiometersand depending on the drive, a potentiometer internal adjustment or trimmers and adjustment external or variable. As for the ohmic value, it is usually printed on the external casing and the most common values are from 100 to 500.
dependent resistance
They are non-linear resistors built with semiconductor materials, in this case their ohmic value will depend on the variation of physical quantities such as the luminous intensitythe voltage and temperature.
Like those mentioned above, it has several types:
- Temperature Dependent Resistance: It has an ohmic value that depends on the temperature. Depending on the type of variation that exists, we can speak of NTC (Negative temperature coefficient) or of PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). If you talk about NTC, then the ohmic value decreases as the temperature increases, while in the PTC decreases as the temperature decreases.
- As for face value of each she refers to one temperature 25°C, being much more precise than conventional thermometers and conventional thermocouples, so they present applications in the regulation and measurement of temperature, control and compensation.
- light dependent resistance: Is defined as LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)), where its ohmic value will change with the light intensity that falls on its surface, despite the fact that the variation is not linear. In the same way, it is stated that they are negative coefficients of luminosity, that is, the more light, the less resistance. Here regulation, control and measurement devices are used that are related to the light, as they are photoelectric cells, detectors for alarms and photometers.
- Voltage Dependent Resistance: They are known as VDR (Voltage Dependent Resistor)it has a ohmic value which varies depending on the voltage applied between its ends. In the same way, it decreases with the increase of the applied tension and they are used in voltage stabilizer circuits and in surge protection devices.
What are the materials with the best electrical resistance and how is it measured?
All of this is known as “Resistivity”, It is the electrical resistance that a certain material has and it is a magnitude of any element that depends directly on its nature and temperature. The most common way to get the value of this resistor is mathematically.
For this it will be necessary to apply this formula:
ρ=ρ0⋅(1+α⋅ΔT)
Where its variables indicate the following:
- p0: It is the resistivity at room temperature, it is mostly 20 °C and its SI unit is the ohm per meter Ω m.
- α: It is the coefficient of each material, it offers an idea of how sensitive it is the resistivity of the material to changes in temperature, mostly this is measured in °C.
- ΔT: It means the difference of the temperature considered with respect to the ambient temperature, it can be said that it is: ΔT = Tf – Tamb. It is taken into account that the ambient temperature is normally 20 °C, so it will be as follows: ΔT = Phone – 20
According to this it can be said that resistivity of a material will not depend on whether it has a conductor of greater or lesser section or length, quite the opposite that happens with the resistance. You have to take into account what the resistivity units, they can be deduced by getting rid of the equation of the resistance itself, knowing that this is also measured in ohms.
Therefore, for this, each magnitude must be replaced by its unit in the international system and this will be as follows:
R=ρlS⇒Ω=ρmm2⇒ρ=Ωm2m=Ω⋅m
As you can see, it is not very common to have the section of a driver in square metersso another widely used unit for resistivity is Ω mm2/m. In order to make direct use of the resistance equation, it will be necessary to enter the length in meters and the section in millimeters squared.
When the temperature is higher, then the resistivity is fulfilled:
- Increase in metals: This means that it drives worse when the temperature is higher.
- Decreases in semimetals: That is, it drives better the higher the temperature.
Depending on the resistivity of the materials, these can be classified as follows:
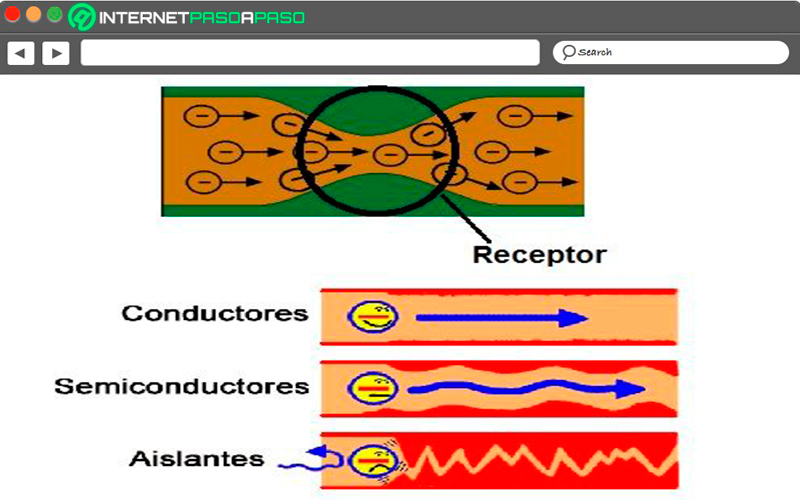
- drivers if ρ
- semiconductors if 10-5 Ω m
- Insulators if p > 106Ω m
Therefore, it can be said that whenever a material has a electric resistance Will have a resistivitywhere mostly the resistivity of metals will increase with temperature, while the resistivity of semiconductors will decrease with increasing temperature.
According to this, here we leave you a table with the materials that have more resistivity:
| MATERIAL | RESISTIVITY (20°C – 25°C) (Ω·m). |
| graphene | 1.00×10-8 |
| Silver | 1.59×10-8 |
| Copper | 1.71×10-8 |
| Prayed | 2.35×10-8 |
| Aluminum | 2.82×10-8 |
| tungsten | 5.65×10-8 |
| Nickel | 6.40 x 10-8 |
| Iron | 8.90×10-8 |
| Platinum | 10.60×10-8 |
| Tin | 11.50 x 10-8 |
| Stainless steel | 72.00×10-8 |
| Graphite | 60.00×10-6 |
Computing