
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you need to know the definition and functions of a bus in computing? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and discover everything about it ✅ EASY and FAST ✅
There is no more notorious work of electronic and computer engineers than the development of the different buses. Thanks to the development of this kind of architecture, today we can have in our hands mobile phones and computers with very large memory capacities and at the same time simple execution with almost instantaneous functions.
A mobile device, on its circuit boards, actually features extraordinary bus designsturning them into true tools that we cannot miss today.
In this article we are going to explain what buses are in computing and we will also detail the different classes that exist for each of them and their different functions. We will also talk about the evolution that these buses had and that are reflected in their different generations.
What is a bus and what is its use in computing?
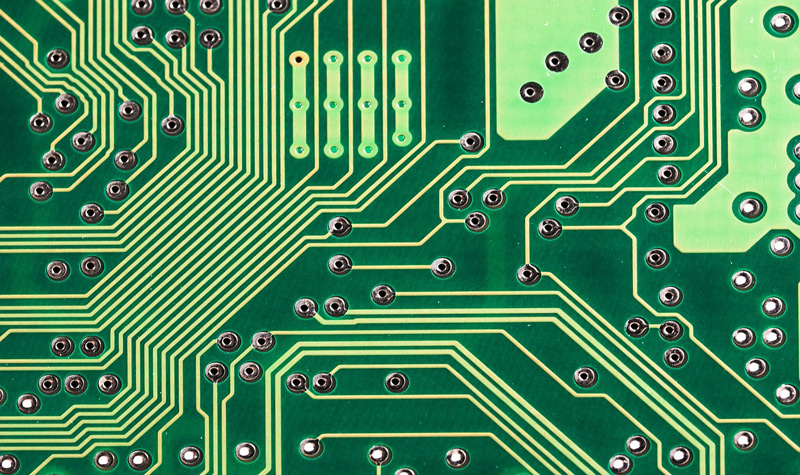
The computer bus is the system by which the different components of a computer transfer and relate to each other the data they share with each other.
This is done thanks to a circuit that is printed on different plates and is made up of cables or tracks, resistors (which are responsible for introducing electrical resistance to certain parts of the circuit) and capacitors (in charge of functioning as an energy storage that those circuits need).
There are two types of data transfer in computer architecture. One is serial transfer which can carry one bit at a time. The other kind of transfer is called parallel which can transfer up to 8 bits at a time.
Channels are currently used to transport several buses at the same time, the most used being the serial type. We will develop this topic more deeply in the last part of this article.
Thanks to the existence of these computer buses, we can get the microprocessor to communicate with the memory; and also ports of entry, such as the keyboard, the mouse and the microphone; Y exit ports, such as monitor, printer or speakers with the different parts of the operating system.
How does a computer bus work? Components and features
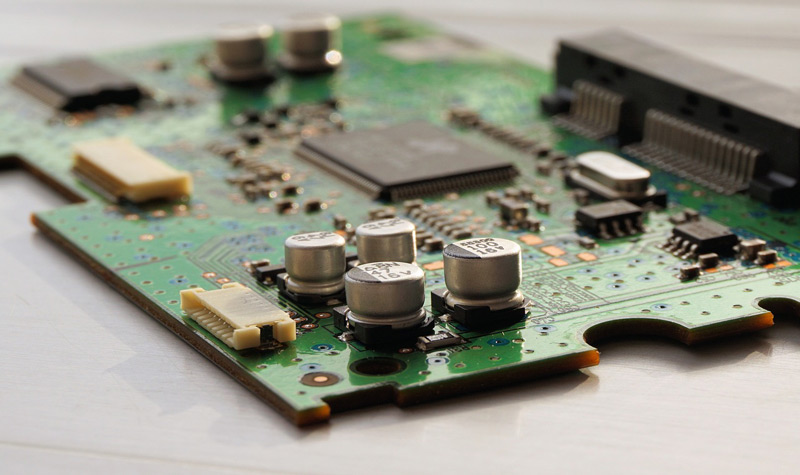
The operation basically consists of passing electrical signals through metallic conductors and being received by another component according to integrated protocols that they manage together.
They can also drive digitized signals and define their capacity according to the number of repetitions they can perform in a specific time, classified by sending that frequency and the width of the data. This relationship is inversely proportional to each other.
The components of a bus are:
- Cableswhich is used to transmit electricity.
- License plate, that has a circuit of paths, tracks and other elements printed with materials that are or are not conductors of electricity. Its mission is to drive and deliver data between components.
- resistors as we had mentioned, they are electronic components that are designed to work as resistance, that is, they analyze the transmission that exists between two points of the electrical frequency, generating a control of the maximum current that passes through it.
- capacitors, They work to be able to store energy and at the same time transmit it to different elements that immediately need electricity. His job is passive.
What are the main generations of buses that exist?
There are different generations of buses that have been modified through the discovery and development of better transfers through the channels.
Next, we will name each of the existing generations:
First generation
This generation develops between the 70’s and 80’s where there were two buses, not destined for memory and the other bus was destined for the different devices that surrounded the memory.
In other words, with this generation the computer worked with two defined areas and with specific instructions and synchronizations for each of them.
Second generation
This stage is characterized by the greater speed and autonomy that the buses had. The most important problem that this kind of generation of passive buses had is that it needed to use the CPU to control the buses, which allocated an important part of it.
The hierarchy between the different buses began to be established according to the degree of frequency. It takes place between the 90s and the beginning of this century..
Third generation
It is the generation that is used today and its most important feature is that it allows point-to-point connections, managing to fragment the routes or tracks through which the data travels, thus allowing the number of connections to be reduced and serial interfaces to be achieved.
It is a relatively new technology, it has been in the computer market for 10 years.
How are computer buses classified? All types
Next, we will talk about how these computer buses are classified according to their functions:
parallel bus
As we told you before, a parallel bus is one that is dedicated to transmitting data one byte at a time and at the same time. It is characterized by a frequency that is small but has a large amount of data being sent.
Its connections are complex and the logic it maintains is simple. It is widely used for those systems where little data or computing power is needed.
These were the most used between the first and second generation, but they had disadvantages in terms of control that had to exist from the CPU.
serial bus
We also talked about it earlier, a serial bus is one that is characterized by being able to transmit up to bit by bit at the same time. Their bandwidth will depend on the frequency where they are broadcast since they are inversely proportional.
They are currently used especially for solid state hard drives because they allow greater efficiency in the transmission of information.
Of control
The control buses are an integral part of the parallel buses and are responsible for transmitting all the data or signals so that you can control the devices that need to communicate.
They are widely used in status indicators, as they can drive each of the components that have shared connections or lines with each other.
Of data
Which can move the bits in a random way so you need a power so you can have data exchange directly with the CPU. You can control the data bus and the address bus in terms of their use and access.
Of direction
An address bus is one that can have a number to assign to a memory or memory cell within main memory, for example RAM.
It is independent of the data bus and can work directly with the microprocessor through a channel assigned for this purpose.
multiplexed
This class of buses is responsible for transmitting electricity sometimes to an address bus and other times to the data bus with the characteristic that they never do it at the same time.
The chipset What relationship does it have with computer buses?
The Chipset is the set of integrated circuits that is housed on the motherboard or motherboard and its main function is to collect data from all processes and send it to its correct recipient.
It is the one that controls different hardware functions and access to memory, among other functions. In other words, it makes the motherboard connect with the most important components that our PC has, making the motherboard the main protagonist of the entire hardware operating system of our computer.
From here we can conclude that the chipset is closely related to the computer buses since without them there could be no communication to collect and send the processes.
In addition, the chipset is also designed with a computing architecture using different buses to be able to connect between its internal components.
Hardware