
How many times did you not hear about Bits, Bytes, Megas, Gigas? Surely a lot, so you may have been left with the doubt of knowing what this is. The aforementioned is part of the Computing Units, which are nothing more than methods that allow us to explain the different sizes in the digital world.
These measures can be grouped into 3, which would be storage to measure the space occupied by the information on the disk. processing to calculate the processing speed of a processor, and the data transmission that measures the time it takes for a server to put the data packet on the line to send.
For many it is a confusing issue, and this is given by all that exist and by the use that is given to each one. Therefore, we have prepared this little article in order to explain a little about what they are and the easiest way to relate and interpret them.
Index:
What is and what is a computer unit of measure?
These are nothing more than the expressions that are used to know the ability of our team to save a file. We must bear in mind that these units are not measures of weight as many people believe, but that they are measures of length. Since actually this tells us how long it is and what it occupies in the space of the unit. Reason why these are calculable by their length.
With them we can obtain data on the storage unit, capacity of memory cards, pen drives and everything that serves to store. But you should know that they are not only used for this, but they are also used to measure your Internet speed and RAM.
In conclusion, they serve to quantify and know the size of a file on our computer, to calculate the storage and data processing capacity of the information.
In the computer storage units the same quantities are also applied as in the physical measurement units, such as kilo, mega, giga or tera; each one is equivalent to one thousand units of the previous one.
What are the main units of measurement we use in computing?
In computing there are three essential units for measuring information, which are the bit, the byte and the hertz. The first two are used to measure space or volume, while the second is a processing speed factor:
Bit
The bit means binary digit and corresponds to the smallest unit of information of a device. This has a value that can be 0 or 1, and with it an infinite number of conditions can be represented binary that could be turned on and off, true and false, present and absent. Usually these are managed to describe transmission speeds.
The magnitudes of the bit are as follows:
- Kilobit; which is equivalent to 1000 bits.
- Megabit; which is equivalent to 1000 kilobits.
- Gigabit; which is equivalent to 1000 megabits.
Byte
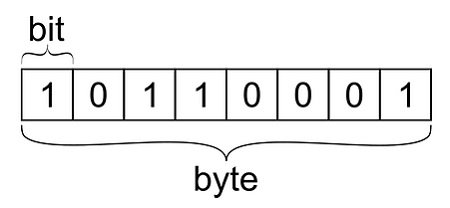
The byte corresponds to the union of 8 consecutive Bits, so this is considered a combination of the first. It should be noted that with it you can achieve up to 256 conjugations, being enough to represent the entire alphabet, punctuation, numbers and more. That is, each character that is entered into a computer is one byte, following the equivalences of the ASCII code.
Example, a document that has 1000 characters, will occupy 1000 bytes. So it is said that the more bytes you have, the more space it will take to save it.
The most important quantities of this unit are:
- Kilobyte; which is equivalent to 1000 byte.
- Megabyte; which is equivalent to 1000 kilobyte.
- Gigabyte; which is equivalent to 1000 megabyte.
- Terabyte; which equals 1000 gigabyte
The relationship between these we will explain in an easy way so that you do not complicate yourself. Let’s imagine this.
We have a large book and a single letter of this corresponds to a Byte, it is composed of eight parts where each one is called Bit. At the time of joining all these Bytes we would form words and with it a paragraph, which would then count as a Kilobyte.
With these Kilobytes we would form the pages and this would represent a Megabyte. So the whole book would be considered the Gigabyte, but if we join this to other books within a library, it would be equivalent to a Terabyte.

Easier to understand , right ?
Hercio

Finally there are the hertz, which is used to measure the speed of information processing. A hertz is the equivalent of a cycle, that is, something that is repeated once, such as the turns of a processor in a certain period of time. That said, you can talk about hertz per second, minute and even hours.
For example, the thin needle of a watch rotates at 1 Hz per minute, while the longest rotates at 1 Hz per hour, and the smallest rotates once per day.
To simplify, hertz also have their magnitudes as they are:
- Kilohertz; which is equivalent to 1000Hz.
- Megahertz; which is equivalent to 1000Khz.
- Gigahertz; which is equivalent to 1000Mhz.
- Terahertz; which is equivalent to 1000Ghz.