
VPN means “Virtual private network” , it is a protocol that creates a tunnel on the web, from a client to a server; in order to hide your IP address at the time you are browsing , giving you greater security. Sometimes it is convenient to hide your identity, to protect the information you send through a public network.
This type of advanced network is combined with Apple technology to monitor , encrypt, update and ensure the security of your device. Keep in mind that it is always important to ensure the exchange of data with the outside and protect privacy, therefore, it is essential to set up a personal private network.
Not all Virtual Private Networks are compatible with operating systems. You must be careful when choosing one of them to operate with the Mac. Some providers of these networks use their own software, but I advise you not to use it. In fact, some countries, such as in China, do not hesitate to block these programs. That said, I bring to you, a very detailed tutorial where you will learn how to configure, create and connect to a VPN on a Mac computer, in a few steps .
Index:
What is a VPN on your MacOS computer?

Allows the user to hide their identity or IP . It acts as a gateway between the operating system and the Internet, providing an absolute guarantee of confidentiality when browsing. The purpose of this is to connect your devices (PC, tablets, smartphones) to a public network, through a tunneling technique, encrypting all the information you send and receive.
This technology changes the IP address , which will guarantee your anonymity, since the data sent and received on your device will be illegible for hackers. In addition to that, there are governments where censorship is strong, with this practice you can skip the blockade, and continue enjoying a free internet.
Steps to create and configure a Virtual Private Network on your Mac computer
Now that you know how useful this type of connections can be, it’s time to teach you how to create one on your MacOS computer, so that you can secure your IP whenever you connect to the Internet and browse or download anything that I liked you So take note and follow the processes that we explain below.
Create a VPN
The first thing is obviously to create the network to be able to use it. To do this, register an account with one of the available providers. For this tutorial, I opted for SecurityKISS , which is a free version.
- Register the provider.
- Enter your email and click create account.
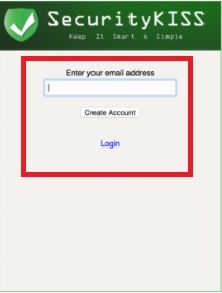
You will receive an email (which will probably reach SPAM) that will indicate the username, password and the secret password that will allow you to connect.
Configuring your VPN
Now that you have created the server for the account, it is time to configure it to start using it without problems. To do this you must do the following:
- Go to “ System Preferences ” on your MacOS.

- Then click on « Network » and then on the small sign «+» and add a new connection.

- Select connection of type « VPN – PPTP «.

- In this window you will be asked to identify yourself and indicate the server address. Then enter your login username and the IP address of the server you chose and click on “ Authentication Settings “.

- Here, you will place your » Password accoun.

- Validate by clicking on « Accept » and finish the configuration by clicking on « Apply «.
Connecting to the VPN server
Now that you have the network created and perfectly configured, it’s time to start the connection process , which if you did all of the above is the easiest part of the whole process. What you should do is the following:
- Before connecting go to: WhatIsMyIp.com and copy and paste your IP address.
- Then, connect to the private virtual network by clicking on the « Network preferences »in« Connect ».
At this point, you will find that your public IP address and location has changed , which means that you already have the virtual network configured. Keep in mind, this step-by-step guide that I offer is for you to browse and exchange files safely. You should use this knowledge with awareness, it is illegal to use this technical type to do fraud , so from now on what you do will be your responsibility.
Most frequent problems and solutions when creating a VPN on Mac
Virtual private networks (VPNs) have a wide range of benefits, but they can also suffer some problems. For example: The network is slow, you cannot connect or it is blocked. For this reason, I bring to you some useful tips to solve these problems .
Use a fast and Premium VPN
If you use a free VPN, it is almost certain that you will get quite low speeds on your connection . Understandably, VPN providers give priority to their paying customers. Even if they say your free private virtual network is as fast as your payment option. There are many affordable services with high speeds, you can see here a list of the best current VPN providers .
Change server
Consider changing the server . The hosting you use for your connection can make a big difference in the connection speeds you get. The closer you are to the server you are connecting to, the better speeds you will get. You can also get high speeds on servers that don’t have many users connected.
Alternate ports
The connection between the computer and the server uses a network port . You can think of this link as if it were a physical port; The computer routes traffic from the VPN server to a specific port, and traffic from other places to other ports. It helps keep packet movement in separate sources.
Even if you think that each port is as fast as any other, you will be surprised to discover that occasionally changing the port to which your private network is connected will get more speed. Some ISPs slow traffic on specific ports , and sometimes you will find that some ports are faster than others for no apparent reason.
Change IP protocols
Most VPNs connect you to a network using the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP is the most common on the Internet , since it includes error correction; If there is a connection problem or some of the data is damaged, the transmission continues, and the equipment that sends the data knows that it must continue to forward information until it arrives correctly.
UDP , although not as common, is noticeably faster than TCP . It does not provide error correction, so if something is lost in transit, it will not send the information again. This reduces the time it takes to transfer information.
What protocols does the MacOS system accept?
Apple is one of the best technology manufacturers in the world, so its computers are very sophisticated when it comes to connections. Next, I mention the protocols used by the operating system :
- AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol , for reliable data transport.
- Apple File Protocol (AFP), is used in server communication
- AppleTalk Session Protocol , it facilitates the asynchronous message to connected clients
- Datagram delivery protocol , is responsible for communicating with other open systems.
- Link Name Protocol . It is used to verify that there are no two computers with the same name
- AppleTalk Echo Protocol . Check the accessibility of the nodes in the network.
- Printer access protocol , to establish communication with this device.
- Protocol routing table maintenance , reports on the network topology.