
UPDATED ✅ Do you need to know what a RAID hard drive is for and you don’t know what it is? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and discover what types, levels and uses exist ✅ EASY and FAST ✅
RAID technology has been used for several years, it is especially used to carry out critical data operations, where not a single bit can be lost. This technology is used especially by professionals or companies that require a lot of care and attention, where losing information can cause big problems. Its main function is to protect user information, thus providing security and confidence.
As usual, we have been used to seeing computers with one or two hard drives, but this technology takes care of combine multiple disks (HD) in order to form a single unit, and all the data handled will be stored in each of them, despite being several, they all work as one. The point of all this is, if one of the disk begins to fail or is damaged, the others continue to work correctly, Thus, your information will continue to work as if nothing happened with the equipment.
Due to the importance of being able to manage and know what a RAID is, “Redundant Array of Independent Disks” here we will show you a little about what they are its levels and its main typess so that you can keep it in mind when you want to implement it in your business.
What is RAID technology really and what applications does it have?

As we mentioned before, this type of technology is responsible for allow connection of 3 or more hard drives simultaneously in the same team, in order to always provide support to the user in the event that there is any type of inconvenience with one of them.
RAID is responsible for unifying all these hard drives, in such a way that it will appear as a single HD. This allows the user to have greater security in their data, especially for those that are really important and cannot be lost, it also allows greater speed for access.
The “Redundant Array of Independent Disks” It is characterized by offering different advantages to each of its users, among them we find the following:
- Take all capacities of hard drives that are connected to form a single volume layer.
- Increase access speed. To do this, separate all the data in several blocks so that reading and writing is much faster.
- When using this technology, storage speed will increase as hard drives deteriorate.
- Offers a high level of tolerance
How many RAID levels are there and what features do they have?
It is important to mention that RAID is capable of supporting different configurationsthey include levels 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 0+1, in total there are 6 levels, each one of them fulfills an important function in its operation. Because of this we will explain each of these levels and their main characteristics.
level 0

It is also known as Stripping and is considered as a data dumping technique. This means that the data will be written to the drive, the same they will break into blocks and will be distributed on the discs that are part of the setwhich will allow higher performance as well as more secure storage.
By making use of level 0, at least one nth of each of the data is going to be found on each of the disks. One of its main advantages is that it will provide a high performance as to writing and reading. But, this level 0 can only be used for those applications that are compatible or withstand loss of data access, which will be possible to obtain from different sources.
Level 1

Level 1 or Replicas, It is one of the techniques most used by RAID technology, and its main function is to provide identical data when writing to each of the hard drives that make up the set, thus leaving a copy on each of them.
This technique is characterized by the fact that it allows a high level of data transfer when they are read, but generally they act independently. In addition, it offers better reading performance. In terms of its storage capacity, it is exactly the same as replicas of hard drives in hardware.
East level 1 is responsible for making each of the discs are identical to each other and among its main applications is Read-intensive OLTP and other transferable data to provide high performance. Applications such as email, operating systems, random access intensive environments, reads, and application files often benefit from this level 1.
Level 2
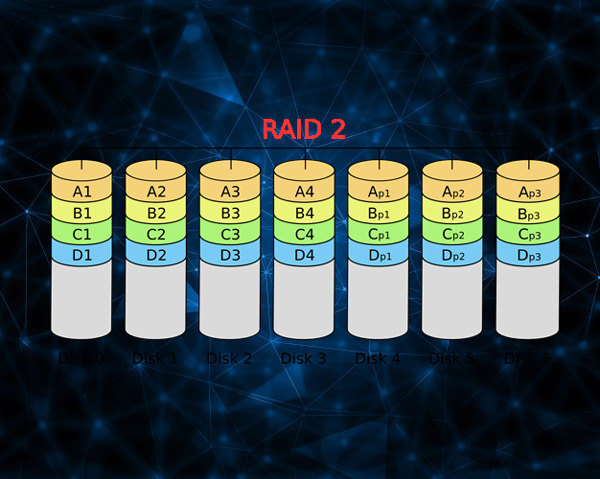
This takes care of detect the mechanisms of failures in the disks of the set to work in memory. That is, level 2 will be in charge of constantly reviewing each of these hard drives. But it should be noted that this level is currently one of the least usedsince almost all the discs or the great majority leave the factory, that is to say new and in general they already have this type of fault detection includedso on many occasions RAID 2 does not end up being necessary.
Level 3

At this level, all the data that is stored on the hard drives is divided among all those that make up the set, but except for one, in which it is responsible for store parity information. All the data bytes have their parity, this is what allows errors to be identified and stored on a specific disk.
This level 3 is characterized by offering a high percentage of transfer as well as a great reliability in the information provided. In addition, it is responsible for providing a very good performance for images, videos, life sciences or any other sequential application. And to be able to work it requires at least the use of 3 HD.
However, it is still not very well suited for those applications that require simultaneous input and output operations of multiple users.
Level 4
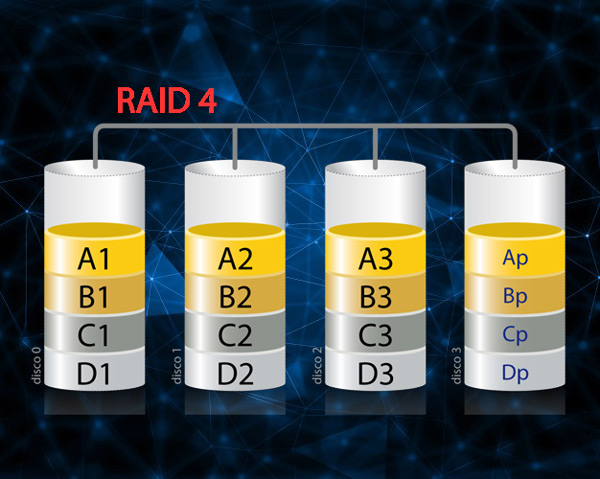
It is responsible for using the parity that is concentrated in a single unit in order to protect each of the data. Level 4 is considered the best for what is the transfer of inputs and outputs and not for transferring large files.
This level is rarely used with technologies such as write cache and with it you cannot perform the installations of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
It can also be said that it is very similar to RAID 3 but this presents is a block parity and it is said to be the capacity of the member disks minus the capacity of one member disk.
Within this level, each of the recording operations that are carried out will require a new parity calculation, this will allow you to have a little more confidence in the storage of the information obtained.
level 5

It is the most common of all and is responsible for distribute parity among each of the member units. Level 5 has the function remove level 4 writing bottleneckthat is, that process which is used to calculate parity. This level is typically used for the write-back cache in order to reduce the asymmetry.
As far as the storage capacity of this level is going to be equal to that of all the member units, the storage capacity of RAID 5 it will be equal to the capacity of all the partitions of each one of the members. In addition, it takes care of reducing the required components when it is providing good availability and a good performance for each of the reads.
Level 0 + 1
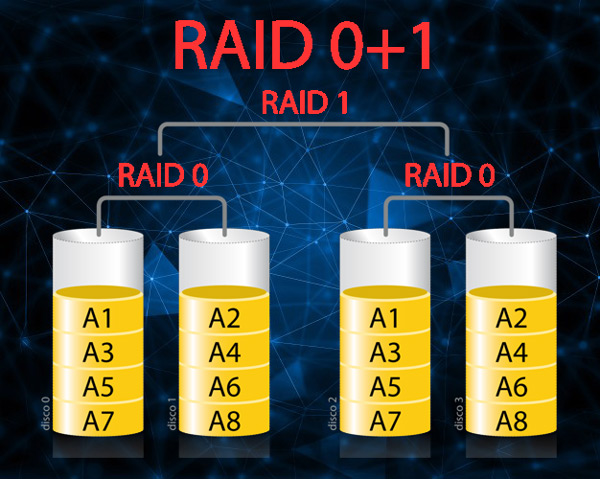
This is one of the most striking, since it is about a combination between what is level 1 and level 0, where the data is going to be divided between them to improve the input.
Another of its characteristics is that they can duplicate all your information using other disks in order to provide a better backup for all the information. In such a way that a good entry can be ensured with level 0 accompanied by the redundancy of 1.
Unlike the other levels, it is that to be carried out it will be necessary the appearance of at least 4 disks to be able to mount what would be RAID 0+1. Its main advantage is that it is the fastest and safest of all, which could be worth using the 4 units necessary to carry out its operation.
What types of RAID are there?
As for the types of RAID we are going to find 2 completely different ones, one of them is hardware-based while the other is based on software. Like everything, each of them has its pros and cons.
hardware-based RAID
It is currently the most up-to-date and this is because it does not have the need to depend on a operating system. In addition, it is quite fast, which allows you to explore each of its resources, but not everything can be wonderful, and as every good thing has something bad, this time is not the exception and that is that in terms of its cost, it is quite high. becomes its main disadvantage.
Another of its aspects is that it usually use devices or also known as RAID controllers, these can be added to computer motherboards.
software-based RAID
Unlike the previous one, this one is not currently widely used, since in terms of its operation it has several disadvantages with respect to the hardware, it is usually much slower in operation, its configuration is much more complex and it depends on a operating system so that you can have a satisfying experience.
However, it should be noted that It is usually much cheaper than the previous one., but if what is sought is quality and good results, the cost becomes aside. lastly this software is dependent on the processing power of the computer being used.
Computing