
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you need to know the definition of CPU and its differences, uses and types? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and Learn everything about computer hardware ✅ EASY and FAST ✅
The Central processing unit of a team is the most important component of it. It is in charge, mainly and as its name indicates, of process any type of information and offer those ports that are completely necessary so that peripherals can be connected to it.
The CPU, as it is called in the computer world, is made up of a series of components that together make the computer work properly. These microunits are arithmetic-logical unit (UAL) and the control unit (UC). The union of both is what is known as a microprocessor, a processor (or, better said, a set of dozens of processors) of reduced dimensions.
In this text we are going to try to solve all the doubts that arise about the concept of Central Processing Unit, the characteristics of its components and its operation. In addition, we are going to define the CPUs that are known and other curious data about this concept, such as, for example, what is difference of a graphics unit or GPU.
What is a CPU and what is it used for in computing?
As indicated initially, the Central Processing Unit (processor, CPU or CPU) is the most important part of a computer and other devices that include it, such as, for example, a smart TV or a smartphone. In fact, it is the place where all procedures related to information are carried out.
It has a structure based on an integrated circuit called a microprocessor, which can and does change between the different brands of computers on the market.
It is a device that interprets a series of instructions that are contained within a program, or, that are defined in the inputs and start the execution of the data process.
It fulfills different functions:
- Program execution. It ensures that their instructions are addressed for their start-up and commissioning.
- Programming. It refers to the interpenetration of all the functions of the system through a prior organization chart preparation. Thus, the saturation of the system is avoided and what it can support at all times at the disk and memory level is controlled.
- Communication with all input-output units. The agreement is made between each of the units, so that the peripherals can respond without collapsing between them and, in general, immediately.
- primary storage. This is equivalent to good memory management, so that it is controlled with the programs that they have the necessary space so that they can function correctly, assigning it to each one that it needs based on its characteristics and the use that is being given to them at all times. .
Top 10 CPUs
Next we show you a list with the 10 best-selling CPUs of the moment so you can choose the best one for your PC.
OFFERBest Sellers No. 1
OFFERBestseller No. 2
OFFERBest Sellers No. 3
OFFERBestseller No. 4
OFFERBestseller No. 5
OFFERBestseller No. 6
OFFERBestseller No. 8
OFFERBestseller No. 9
OFFERBestseller No. 10
Evolution of the CPU concept
In the first computers that existed, the central processing units were designed to work with a much larger computer. For this reason, the machines were handled with very simple, mechanical mechanisms. In fact, at first, these computers had to be rewired so that they could perform different tasks.
The first computers with a CPU were stored-program computers.. This was established with the ENIAC model created in 1945 and whose architecture was prepared by the mathematician who has marked the world of computing, John Von Neumann.
What was intended with this team was to perform operations of different types that were stored in the computer’s memory, which meant no physical changes needed in the wiring of the computer to avoid wasting time and effort and errors.
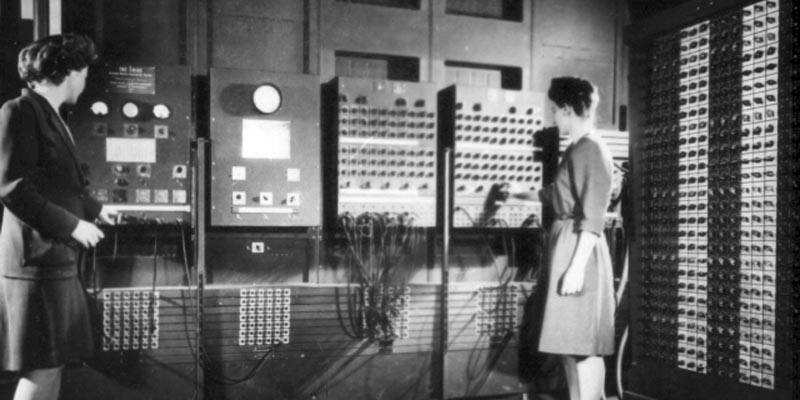

Initially, the central processing units were created to measure, but this is not very operational and, for this reason, Standardization of processors to suit various purposes has long been considered. This was made possible by the advent of the integrated circuit (IC), which has allowed CPUs to become increasingly complex in small spaces.
We must get used to the fact that today microprocessors are found everywhere, from cars and trucks to mobile phones or children’s toys. The beginning of improvements for this type of units It started with the appearance of the transistor in the 1950s.. With it, more complex CPUs could be created on printed circuit boards.
Those based on integrated circuits are referred to as small-scale integration (SSI) devices. These contained transistors always multiples of ten. Complete ones required thousands of individual chips, but consuming minimal space.
In 1964, IBM introduced the System/360 architecturewhich It allowed a series of computers to run the same program at different speeds. Therefore, although the computers were incompatible with each other, the architecture was the same. At that time, it he was able to verify that the transistors allowed the processor to operate at much higher speeds for the commutation time that it offered them.
With the passage of time, the concept of microprocessor appeared for processors made with a small number of integrated circuits; usually only one. The decrease in size made switching times faster. For this reason, the design complexity and size has not changed much over the years once the appearance of this microelement occurred.
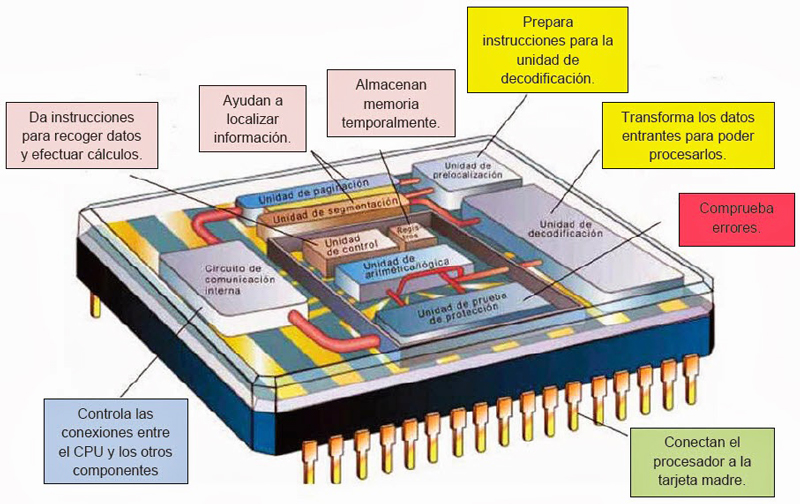
Components and characteristics of the computer’s CPU. What hardware parts make it up?

The Central Processing Unit is made up of a series of components that we will define separately to know the scope of its functionalities:
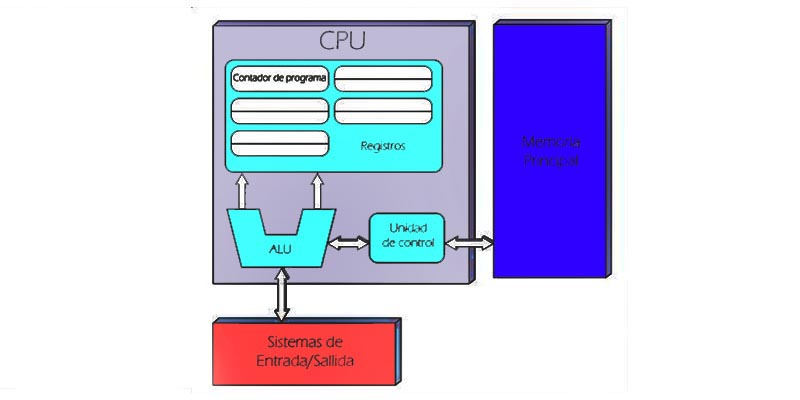
Control unit
It is one of the blocks that make up the CPU. Its main function is to look up instructions in memory, decode them, and execute them through the Processing Unit. In other words, UC is everything the set of circuits that control the flow of data that occur in the processor.
There are many components found within this block. These are:
- instruction register. Place where the instruction is stored during the time it is being executed.
- program counter. Contains the memory address of the next instruction to be executed.
- controller and decoder. It interprets the instruction extracting the code of the operation that has to be carried out.
- Clock. It provides electrical impulses at intervals with a certain constancy.
- sequencer. Generates microcommands that are necessary for an instruction to be executed.
Process Unit
This is another of the most important blocks of this element. Its function lies in execute all tasks passed to it by the control unit.
To carry out these processes, you need the help of the elements described below:
- floating point unit. It is used to perform mathematical operations with real numbers.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It is used to perform basic arithmetic operations, logic functions, comparisons or bit rotations.
- status record. It saves some indicators about the result of the operations that have been done.
- accumulator register. Preserves the operands and results of operations.
Records
A record is a high speed memory integrated within the processor itself. serves for retain data temporarily and be able to access the values most used. In fact, it is the best way for the system to preserve data. Registers are measured by the number of bits they allow to store. If your computer is, for example, 64-bit, this indicates that 64-bit records are allowed to be stored.
The types of records that exist are the following:
- floating point registers. They store data in floating point form.
- constant records. They have values that are created to be used in read-only mode. They are elaborated when the hardware itself is created.
- data records. They hold whole numbers.
- memory registers. They store only memory addresses.
- Specific purpose registers. They hold information about the state of the system, such as a stack pointer.
- General purpose registers. They retain both data and addresses. They are mostly used in Von Neumann architecture which, on the other hand, is typical.
Input and output bus
The bus is used for transport data between components from a computer. They are clues about integrated circuit that can be transferred in two ways:
- Parallel. The bus allows several bits to be transmitted at the same time.
- Series. The bus can only transfer the data bit by bit through a single cable transmitting information.
In the first computers, the buses always worked in parallel, but in recent years these have been replaced by serial buses. Although the latter are more difficult to implement, the transfer speed they achieve is much higher.
How does a CPU work?
This performs multiple operations, but what stands out the most is the program execution. The programs, seen from the inside, are a set of instructions that are represented by numbers that are stored in the computer’s memory before being executed. All systems that have Von Neumann architecture execute four steps to carry out its operations. These are read, decode, execute and write.
FETCH (Read)
During this step, the instruction represented by a sequence of numbers is collected of the memory.
The Program counter (PC, not to be confused with personal computer or Personal Computer) is in charge of store memory address Where are these instructions?
After reading, the PC is incremented to change position and locate to the memory unit where the address of the next instruction is located which should run. In this case, slow memory is used and its response speed is related to the computer’s cache and processor.
DECODE
Once we have the instruction, this is divided into different parts that will be interpreted by the units of the processor. A part of the numbers indicates the operation to be performed (opcode) and the following parts correspond to information related to the execution of said operation. For example, in the case that the instruction is an addition, it will be necessary to understand the operator that indicates addition and the operands that are intended to be added.
These can be defined by a value or by a memory address, from where the data to be added is taken. In more complex CPU’s, a microprogram that translates the instructionsso decoding becomes easier.
EXECUTE
By the time this step arrives, the processor connects with its units involved in the instruction so that the operation can be carried out that is requested in the program.
When the addition operation discussed above is performed, the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is connected. to carry out the operations, with the inputs and outputs where the numbers to be added are found and the place where the result of the same is placed.
WRITEBACK
In this step, only results are written of the executed instruction. These can be kept in volatile memory or kept in main memorywhich may be a bit slower.
After finishing the last step, the process is repeated with the next instruction cycle in order to read the next one and increment the program counter. In complex processors, multiple instructions can be read one at a time and then executed.
How many types of Central Processing Units are there?
There are several types of Central Processing Unit, which are classified according to the number of cores it has:
single core cpu
It is called CPU core. It appeared with the beginning of computing concepts. It was about a processor with a single core, where the execution of basic tasks was very slowbeing carried out one by one, although at that time, as you can imagine from what we have already mentioned, it was a revolutionary team that allowed for a considerable reduction in the percentage of errors as well as the diversion of resources to other tasks.
dual core processors
It was quite a breakthrough in the world of technology: combine two cores within one processor; it was not an easy task. You have to control the overhead on the management system, which doesn’t allow you to double the speed of a processor.
They were used in multitasking environments since, in it, programs and threads fight for processor time. If a second core exists, one of the threads would run on one machine and the other on the other. Is CPU offers 75% higher performance than a single core processor, not being able to speak of a performance that doubles. Of course, it works two tasks and it does it faster.
Quad core CPU
This is a type of processor called a quadcore. It is made up of four nuclei and it’s much faster than the previous two models. It is capable of performing several tasks at the same time and at high speed.
In general, it is the type of processor that we find in mid-range and mid-high-end mobile phones.
Six and eight core CPU
These are the ones currently used in computers. Are able to perform a large number of highly demanding tasks at breakneck speed. Depending on their capacity, they can run between six and eight main tasks at the same time without the user experience being lackluster.
What differences do we find between a CPU and a GPU?
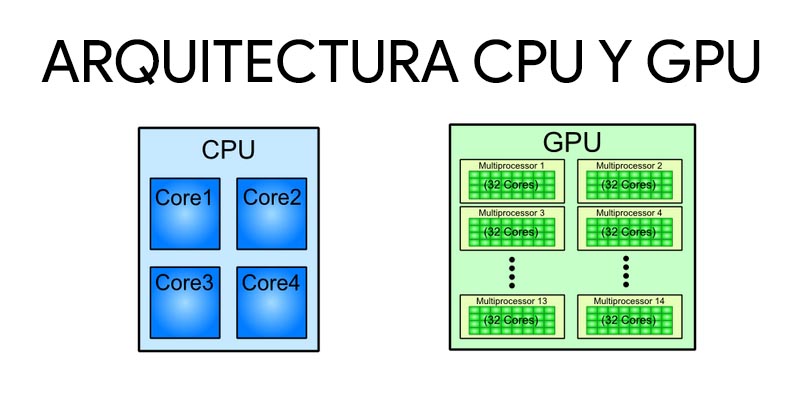
Let’s start by letting you know that, in both cases, we are talking about processing units. This means that the purpose of both is the same: to process.
However, the difference is clear:
- The central processing unit takes care of, redundancy, process all types of acts and information, being of a general purpose or nature, working in series. You can work with graphic elements. The number of processes it loads with is smaller.
- The GPU works specifically on the processing of graphic elementsthat is, image and video, and it does in parallel, according to the Surrounding Model. This supposes take load off the processor, which is free to work on the rest of the elements. For this reason it is interesting to invest time is to choose a good graphics card so that the processor does not collapse, no matter how good it is. Load with many more processes but must be specific.
Hardware









