
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you want to know what are the functions and characteristics of this type of computers or PCs? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and discover the types ✅ EASY and FAST ✅
Computers and personal computers, so common today, have a beautiful story behind in which constant work, plagiarism (and clones) and constant innovation are its protagonists.
Let’s see what exactly is a PC or personal computersticking to what the concept itself refers to, what makes it up, where does it come fromboth as and idea as already entered in computational matters, of what great historical milestone has it been a part andof course, What can we use them for today?.
You will be curious, to say the least, to see how the sector and the concept developed until we got to where we are today and, without a doubt, it will serve to assess the work of dozens of experts for almost a century. Let’s go there!
What are Personal Computers in computing? Definition
A personal computer is a non-shared computer equipment of small dimensionssuitable so that it can be used at home, which works entirely digitally and that has the capacity to process the needs of a user and solve them exactly, satisfying the needs of this at a basic and general level whenever it is given an individual use.
Although the first devices were far from being what we know today, we cannot avoid verifying that, in effect, the essence, and with it, its parts (although now modified) are essentially the same. So we have to a personal computer are constituted, minimally, by:

- motherboard: It is the piece in which all the others fit, by slots, the one that unites them and gives them life, from the most basic to the most innovative hardware elements.
- Processor: It is a component that, as its name suggests, works to process all kinds of information that runs through the computer, from the start to the secondary tasks.
- heatsink: It is the element that dissipates the energy, in this case, heat, that the parts produce when they are in operation. In this way, the temperature is kept in an acceptable gradation so that the equipment can work.
- RAM: This is the fast access memory, so to speak, which is used as an escape method and takes part of the load of the operation of the computer.
- HDD: It is the piece of hardware in which we can store elements, the storage memory. Previously, a hard disk was not necessary as such, since the concepts of computers were very different, but nowadays every computer has, in fact, part of its hard disk already occupied by software that is previously installed and is also used for functions that we, as a user, do not even see.
- Power supply: It is the element that supplies energy to the assembly.
- Peripherals: Although they are not necessary to make the computer work, there are some necessary so that we can obtain information from it and vice versa: mouse and monitor at least.
- Cabin: It is the box in which these and other components are kept. It has a specific shape to comfortably place the elements that we have seen optimizing space.
Obviously, nowadays, with the needs that users have, we look for much more and we end up incorporating more elements: network cards, graphics cards, speakers, CD and DVD readers and recorders, card readers… However, for the computer to work none of this is necessary.
The 10 best-selling Personal Computers
We know that when buy your pc it is difficult to choose one, that is why we will show you below a list with the 10 best-selling personal computers of the moment so you can choose the one that best suits your needs.
OFFERBest Sellers No. 1
OFFERBestseller No. 2
OFFERBest Sellers No. 3
OFFERBestseller No. 4
OFFERBestseller No. 7
Bestseller No. 9
OFFERBestseller No. 10
Source
If we look back we realize that the origin of the personal computer is as old as we want to considerthen, in one way or another, we can always somehow relate the main milestones of computing.
In any case, most will agree that the Datapont 2200 was the first device with an idea from which the PC could start in terms of dimensions, capacity and “peripheral” elements.
It included a multichip CPU, a long screen and a thick keyboard.all of this embraced by a casing that unified it.
The Xerox Altos and Xerox Stars also had much of what you could identify today on a computer. like graphical user interface, desktop metaphor, mouse usage, bitmap display, servers, ethernet connection…
History
The idea of a personal computer appears when the computer is demanded by an ever-widening public.. First large corporations, then laboratories, large businesses… The only thing left to do was give it a domestic use. The concept as such will first appear in the New York Times in what was embodied in the words of those who JW Mauchly thought about the future of the sector.
The first model conceived as such is Programma 101from the Italian company Olivetti, which developed it between 1962 and 1964. This was the device that helped man reach the Moon in 1969. See all generations of computers full.
It was in 1977 that Commodore and Apple launched two devices that they promoted as personal computers.the PET 2001 and the Apple II respectively although, if we have to be honest, the one that we have all always considered the predecessor of the personal computer is the IBM PC.
The point that makes these three devices (and not Olivetti’s) the ones known as the first personal computers is the appearance of the spreadsheet, which turned these teams into work toolsfirst office and then domestic.
Of the three models, millions of copies were sold and the end of the decade was marked by the appearance of dozens of types of personal computersof all kinds of brands, which were rivals at a time when manufacturing them was quite cheap, which meant that by the beginning of the next decade everyone had a PC at home.
Evolution
The evolution of computing equipment has been quite rapid if we consider what each feat involved at the time. So much so that its evolution is given in generations differentiated, five that we have been able to study and the sixth, in which we find ourselves. Of them, it is the fourth that includes the appearance of the PC or Personal Computer.
Infographic: A brief history of computers
generations of computers
Just as we have come to classify the feats of industry, historically calling them “industrial revolution”, computers have also been so important that they have their own classification, this time, by generations.
First (1940-1952)
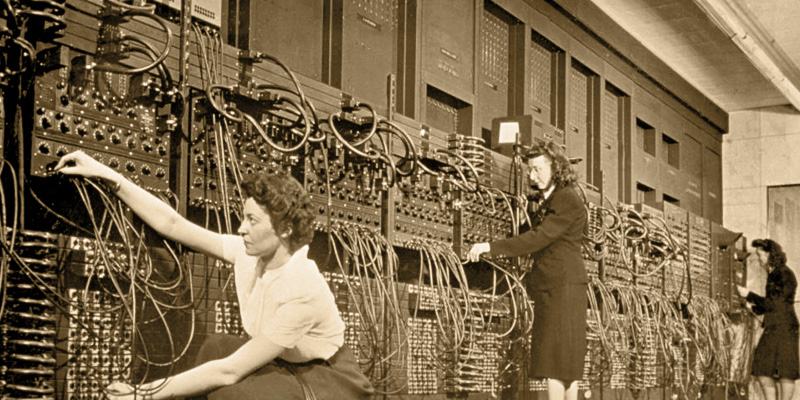
The first computer generation starts in the year 1940when Accurate results are beginning to be obtained with the use of machines in completely digital processes. These tests were, considering the time, quite fast.
In six years appears the one who has taken the fame of first computer, the ENIAC, built with valve electronics and working with the most basic machine language that we have known. Impossible to reprogram and 30 meters longwas an experimental project and never a production model.
In 1949 another prototype appeared, also a laboratory one, never intended to be launched but rather as an element to test the advances in the sector. We can say that the EDVAC was the first device that is related, in terms of ideas, to those of a current computer.
In 1951, the first computer in history, the UNIVAC I, went on sale., which, by the way, was the first product of the company behind it. Obviously, neither you nor I bought it; the client was the US Census, with a purely mathematical purpose of counting.
Two years later, the first-selling computer for a long time appeared on the market, the IBM 701.
Over the years, IBM continues to lead both in sales and innovation and launches the magnetic drum, an idea that ended up evolving into the magnetic disk that we all know.
Second (1958-1964)
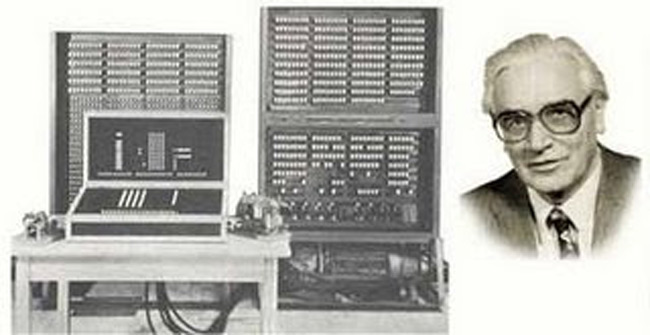
The milestone that gives this denomination is the substitution of vacuum valves in the manufacture of computers, which now have transistors. This means that the devices are considerably smaller and therefore consume less energy. Watch second generation computers here.
Now, computers have passed to work with high-level language, more complex than the previous machine language used. This is possible thanks to the work of maurice wilkeswhich invents what is known as microprogramming, simplifying the development of computational units.
Again, the protagonist was IBMselling the first magnetic disk system, developing what was the first high-level programming language, known as FORTRAN Y unveiling the IBM 1401 mainframe, of which it sold very large units, making it the most successful in history.
In 1962, work was done on the first computer game.which was Spacewar!
In 1964 IBMagain, it launches a family of computers with the same software and different characteristics at the same time that it launches the microprograms commercially.
Third (1965-1971)
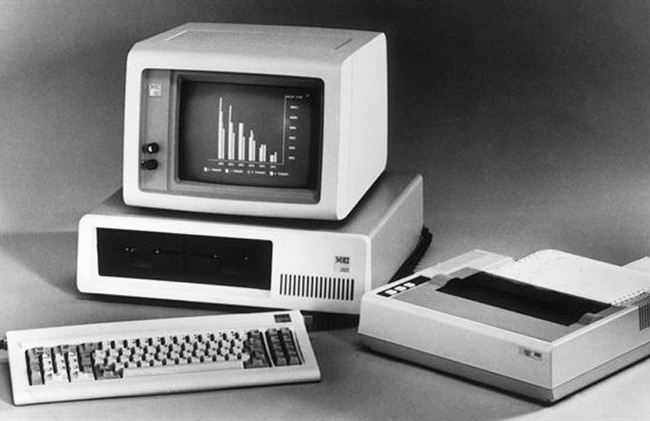

The third generation of computers is given with the use of silicon wafer integrated circuitsa fact that allowed the processing to be much more capable while reducing both machine volume and costs.
Almost immediately after, when only one model with these circuits was popular, microprocessors appear (the first was the Intel 4004). Watch third generation computers here.
It was the combination of both elements that made it possible to pack small transistors and more elements in the same complete circuit chip, which, in turn, achieved an unthinkable efficiency in relation to the assembly of devices.
A way of programming was also introduced that is still maintained today for large computers, which shows us that, indeed, this was a very successful revolutionary change.
The new computers, known as “series” completely ousted all the previous ones, being more reliable, flexible and precise.
Fourth (1971-1980)
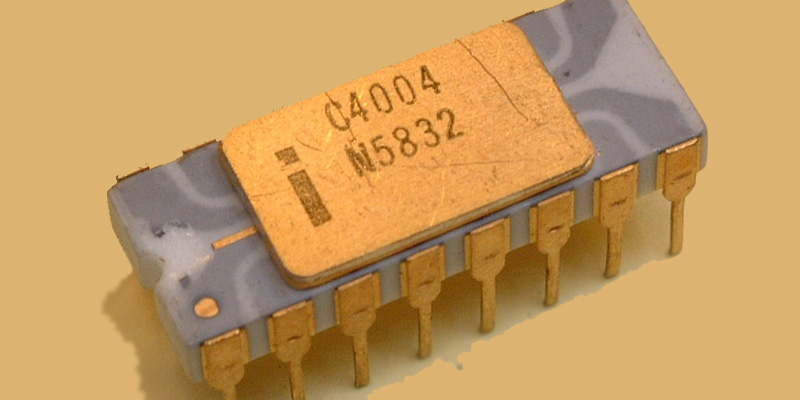
In this fourth computer revolution we have a knowledge and development of the microprocessorof very recent appearance (so much so that it was hardly known at a social level), and chip development, which, among its multiple applications, replaces magnetic ring memories. Watch fourth generation of computers here.
Another essential aspect that marks time is the development of personal computers, that is, the machines we are talking about today, the small equipment for the home user. This is made possible, in fact, by the reduced size that had been achieved for chip microprocessors. There is also a significant boost to the supercomputers.
Fifth (1981-2000)

There is a new revolution, totally overwhelming, with the appearance of the first laptop. In view of the unstoppable advance of technology in the computer field, software efforts are multiplying exponentially. Watch fifth generation of computers here.
Japan took the lead in what is known as a true mission in which artificial intelligence (although at the time the concept did not even exist) would allow us to work with teams that really offered experiences to the user. The project was a failure during the time it lasted, although it is clear that from the moment it was known where the steps should be taken. Milestones of the generation were CD drive and clone re-standardization.
Sixth (2000-present)
The emergence of wireless connectivity it marked the beginning of a new generation in which we still find ourselves. Hand in hand come improvements in connectivity, in network cards, in equipment designs, in the development of phones and the appearance of truly intelligent elements. Watch sixth generation of computers here.
What are they for and what uses do personal computers or PCs have today?

Answering this question is very easy and very difficult at the same time. It’s simple because, nowadays, a computer is useful for practically anything, and if it doesn’t allow us to do something, at least it teaches us how to do it.
Storage
One of the functions that they currently have, although it is not, by far, the main one, is to serve us as digital content storage location. This can be generated by the computer itself, by ourselves working on it, by other people and downloaded and even generated by us with other devices and launched to the computer so that it remains there.
We are talking about images that we take to make a cover of a work, photos that we take with the camera and we pass them through cable, videos that we have liked and have downloaded from our streaming provider, text documents that we have written and have considered saving. to consult them another time…
Intermediary with other devices
We have already seen that we can, from our camera, pass our photos to the computer. That is, It serves as an intermediary between us and the other devices, helping us in some way with the digital products that are handled.
In this particular case it would be to store the photographs but we can do much more. For example, if we connect it to a printer we can make a digital document go into physical format. We can also transfer audio tracks to a CD and enjoy it on the stereo, in the car…
Entertainment
The bulk of the population uses the computer as entertainment element. Why? Very easy. Today the options are counted by hundreds. Can play video games both online and offlinewith friends or by ourselves.
Can listen to music from audio track providers or video platforms, chat, create profiles on social networks and meet people, paying them every day with our experiences and occurrences, write a blog, make entertaining videos ourselves or enjoy the creations of famous and unknown, draw, watch series and movies (online or downloading them), connect the equipment to the television to multiply the entertainment experience…
work activities
On the other hand, this device also gives us the ability to carry out activities that enable or facilitate the work of many professionals.
Write letters, send emails to clients, partners and the workforce, create design elements for our brand image, do accounting, manage resources that we have in stock, search the internet for resources to hold the next company party, schedule appointments with clients, capture the information of each meeting… Much of what you can think of you could do with a personal computer.
Domestic activities
Of course, there are activities that fall in the middle, which are neither leisure nor work, those called domestic. We can do things as diverse as create notes for the shopping list and transfer them to our mobile (or print them if we feel like it), make a presentation for our final degree project, check our email, look for work on the employment web platforms…
Internet access
We have already seen it in the previous points but, of course, nowadays it is very difficult to find a computer that is not connected to a network. The low price of monthly internet connection fees and the amount of information and resources it offers us makes us all connect.
Really, on the internet we can do everything we have seenWell, there are programs to write texts online (and that are stored in the cloud, without taking up space on our hard drive), there are games that connect to the network, others that are found directly on web pages…
But also to be able to do everything that we have already been seeing, we can really use the internet to learn about anything. Search for a recipe, where the nearest cinema is, curiosities about a particular aspect, all kinds of information about a topic you are working on, information about your last name and family lineage, about the weather in the next few days … It’s amazing all that the networkwhich we access from a personal computer (and from other devices) can offer us.
List of the 10 personal computers that marked the history of computers
Although, without a doubt, in the first years in which user computers were launched, all of them were special and surprising, since any small advance that we can consider now before was quite a feat, it is true that there has been a set of devices that, without a doubt, they have made history.
Apple II

Indeed, the first computer that made history is from Apple, launching in the year 1977 and remaining on sale in all markets until the middle of the following decade at a price, in fact, accessible to the average user.
Some of its features include Apple DOS OS, 4KB of RAM (later launched with the inconceivable amount of 64 KN), a MOS Technology 6502 processor running at 1 MHz and charging and saving program elements on audio cassettes.
This model made the world of technology see how important open architecture is. Also, stood out for having expansion slots that made it possible for the connected peripheral cards to control the bus, since it got dozens and dozens of manufacturers to join together to launch new hardware.
Disk II design by S. Wozniak is the icing on the cake; one expansion-slot pluggable external floppy drive for faster data storage and retrieval. It would be curious to know that it has been the most cloned computer, with 181 known clones.
IBM PC

IBM launches its product four years later, in 1981, the predecessor of what we know today as the PC. It was made up of an Intel 8088 at 4.77 MHzan 8288 controller, a BASIC interpreter for the ROM, which was 8 KiB and capable of up to 64 KB of RAM divided into four banks.
Worked with expansion cardswhich the brand called adapters. Curious that it was sold without any built-in expansion element, which forced us to buy any of the ones we wanted to attach. In general, the firm’s hardware worked very well, although it was in terms of graphics that very good competitors came out very soon.
The fact of having a socket in which a coprocessor could be mounted stands out. numeric with which it could be calculated in floating point. This computer also became well known for its much superior keyboard.which even won a design award.
Commodore 64

One of the first and also one of the best-selling in history, it could not be missing from this top of personal computers that are part of the history of technology and computing.
curious his cathode ray screen as well as its robust keyboardwas accompanied by a 64 KB RAM and an audio and graphic system much superior to those of contemporary equipment.
Highlights were the direct connection (and numerous) for peripherals and the huge number of video games, an aspect that has made this PC even today referred to as a video game console. As in the case of the Apple II, this computer was cloned countless times.
Compaq Portable SLT/286 1903
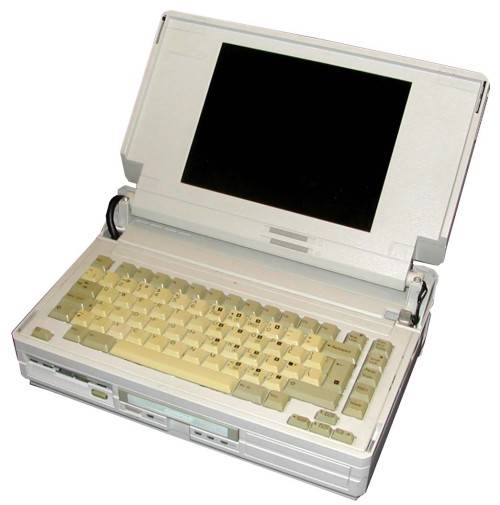

The first laptop which came out on the popular market in 1983, very well sold for being the first, also, completely compatible (outside of IBM) with the highly valued IBM PC at the time.
Among its characteristics we can mention a graphics chip that displayed characters in 9×14, allowing a change of scanlines on the monitor. This made it an essential for working on spreadsheets. Compaq paid Microsoft to license MS-DOS and used reverse engineering to copy the IBM BIOS, investing in it a million dollars. Its 128 kb Ram was expandable and had an Intel 8088 processor.
macintosh

It superseded the Apple II as a standard shortly after it was launched on the market, in 1984. Of course, we have seen, over the decades, several models of these computers, although the first, which was already quite a hit, was the Macintosh 128K.
This was a very famous unimodule for being the first to integrate, as part of the set, a graphical user interfacewhich was allowed to be tested perfectly with two softwares as they were MacPaint and MacWrite, predecessors of what is now a computer suite. The inclusion of the floppy disk in 3 1/2 was also much talked about.
As faults, the lack of fan, even though it had been proposed to S. Jobs, and the slowness of the computer. Even so, it was a highly praised bombshell and, as we say, capable of unseating another model of the firm itself.
The processor was the Motorola 68000, RAM was 128KBquite a leap compared to the previous one, had RS232 and RS422 serial ports as well as a 9-inch screen.
IBM XT 286

This model was already talked about before it was launched due to the fact that those responsible for IBM had moved to Mexico for its production.
Designed to replace your own IBM PCit did so thanks to the inclusion of a greater number of expansion slots, hard disk, more power in the power supply, a motherboard with more memory and with the remarkable elimination of the cassette interface.
As a processor I had a Intel 80286 ran at up to 6 MHz, which made it by far much faster than the ATs that were being sold at the time. Other features were a 640 Kb RAM and a 20 MB internal hard drive.
Toshiba T1000, T1100 and T12000

In the year 1985, a series of models of mass consumption laptops are launched by Toshiba. To make them lighter, the hard disk was dispensed with, so that any program had to be run on floppy disks. It also caused a lot of talk, although simply because of the novelty, not because it meant anything important, the LCD type screen.
ThinkPad
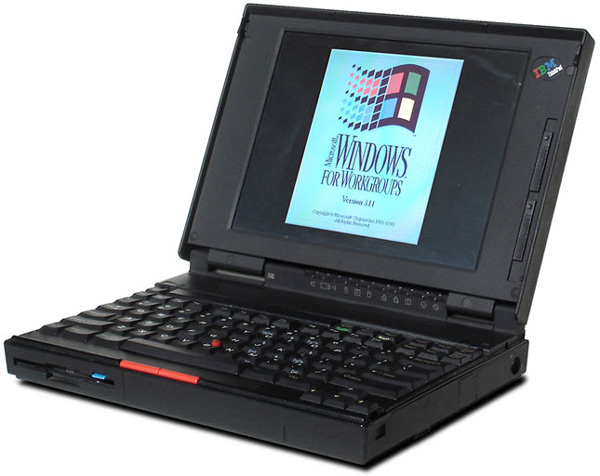

This series of laptops has stood out for becoming corporate favorite. They were marketed in the early 90’s and achieved more than three hundred prizes with just three models.
Especially striking was the TrackPoint, antecedent of the touchpadwhich made the concept of a laptop a little more real, since it is nothing more than a version of it (a red button that was in the center of the keyboard).
It was with them that we saw the first Intel Pentium I in a portable computer. Some of its models incorporated a floppy drive and a CD reader and began to use operating systems that are currently known as Windows NT4 and, later, the famous Windows 95.
iMac G3
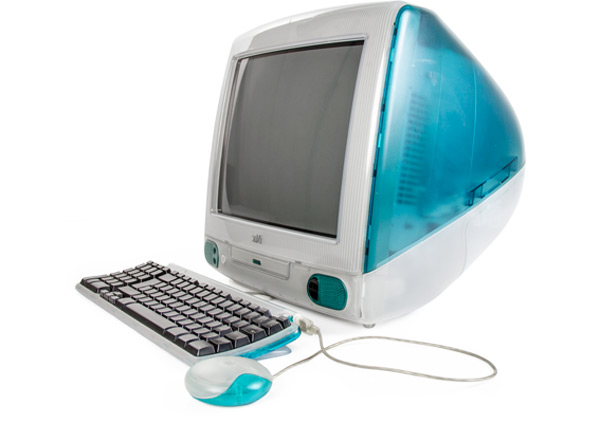

Without a doubt, the most revolutionary aspect of this device was precisely that, its appearance: a computer with a fully casing rounded (as much as possible to maintain the current form of these teams), as well as being colorful (up to 13 designs in different colors were released between 1998 and 2001) and translucent.
Comparing it with the rest, its ability to 128GB storage, although considering the models of the time (1998) it is not so much either. It had a disk drive and it was the first computer that became really famous. It had a USB port..
Asus Zenbook UX21E

Although Apple was, as on many other occasions, the first to launch an ultrabook, it was Asus who made the difference by launching this device with an SSD available from 64 to 256 GB. It also made available to the user Intel i3, i5 and i7 processorsknown for offering solutions to any need.
Hardware

















