
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you want to learn how to open the Windows 10, 7 and 8 task manager and all the functions it has? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and discover how
Task manager is a tool built into Windows operating systems. The same brings with it a lot of information useful when measuring the performance of the computer and the system itself.
has always been used by average users to end applications or programs that are frozen. But the truth is that there are many more things that can be done with it, such as seeing and controlling the activities that are running on the computer.
That said, if you want to know all the functions of this powerful tool, We invite you to stay with us in this entry. Where we will also explain the different ways you have to open it.
What are all the functions of the task manager of my PC?
Beyond what is mentioned above, it is used to monitor performance, check the status of the network, see the users connected to the computer, etc. So that Knowing what exactly this plugin helps you with is key to being able to control 100% the functionality of our computer.
Next, we will see in detail what its main functions are:
Measure processes
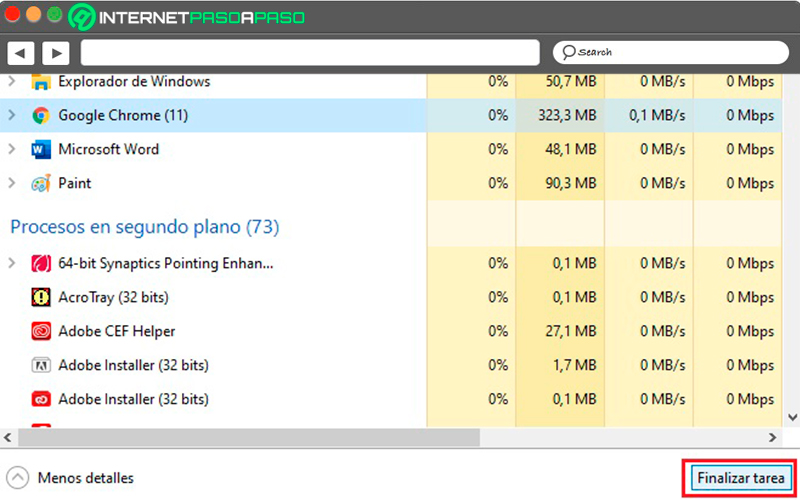
When opening it we can see that it has different tabs, where each one provides different information. The first we can see is “Processes”, it provides us with the consumption information of each of the applications. This includes:
- ongoing applications, displayed at the top as “Applications”.
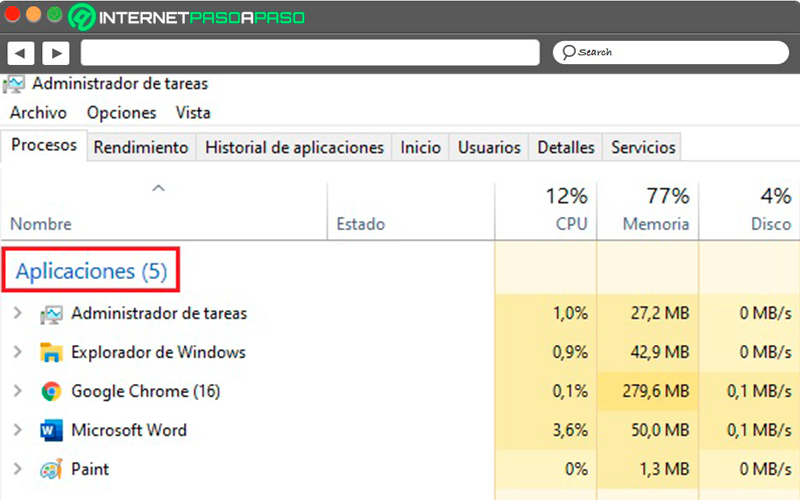
- background apps, displayed as “Background Processes”.
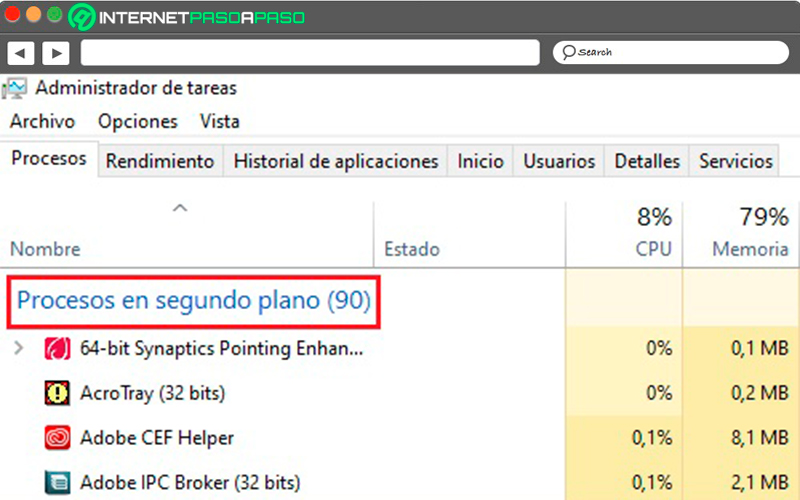
- Finally, we can also visualize the “Windows Processes”.
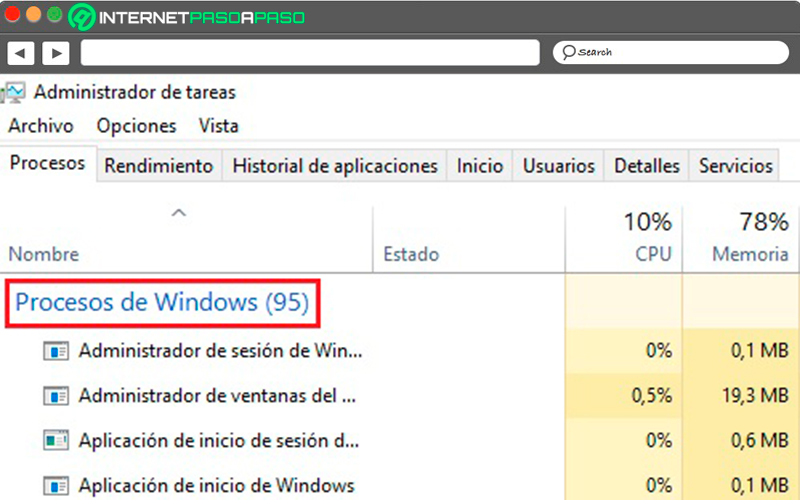
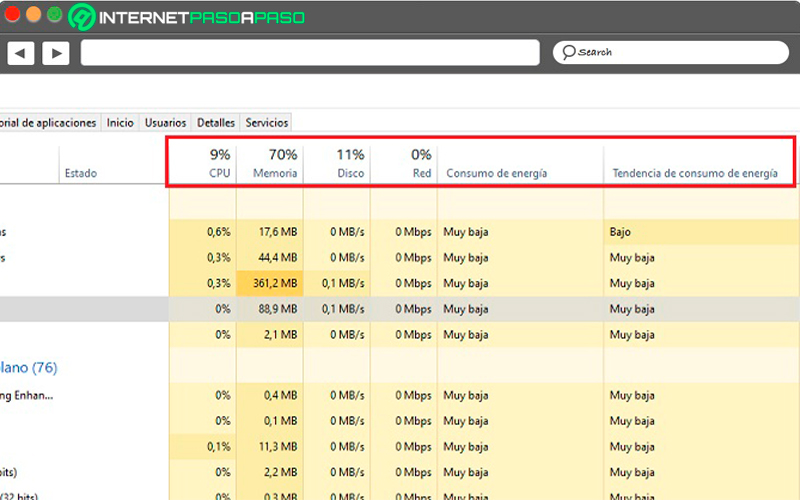
From each of the 3 different types of applications that are working on our computer, the following data can be observed:
- CPUs: the general consumption in CPU that is causing the application in question. This comes in percentages and is measured after having measured the consumption of the application on the hard drive and in RAM memory.
- Memory: In this table, the RAM consumption caused by the application, service or process being evaluated is measured in Megabytes.
- Disk: In this section you can see the requirement in percentage of the hard disk. In this application, each second that passes is measured in MBps.
- Net: if it is an application that works with the Internet, for example, a Web browser, here you can see how much consumption is generated in Mbps.
- Energy consumption: This panel, according to all the expense observed in the previous lines, shows how much energy this application or process requires. All this is measured at the same instant.
- Power Consumption Trend: Unlike power consumption, this panel shows the average consumption of the application or service over time.
- It should be noted that it is from the tab “Processes”where the famous action of “Finish homework” that we use so much when some program does not respond.
Measure overall performance
In the second tab which is called “Performance”, We are going to find a general overview in data graphs about the state of the most important components of the equipment. Which are:
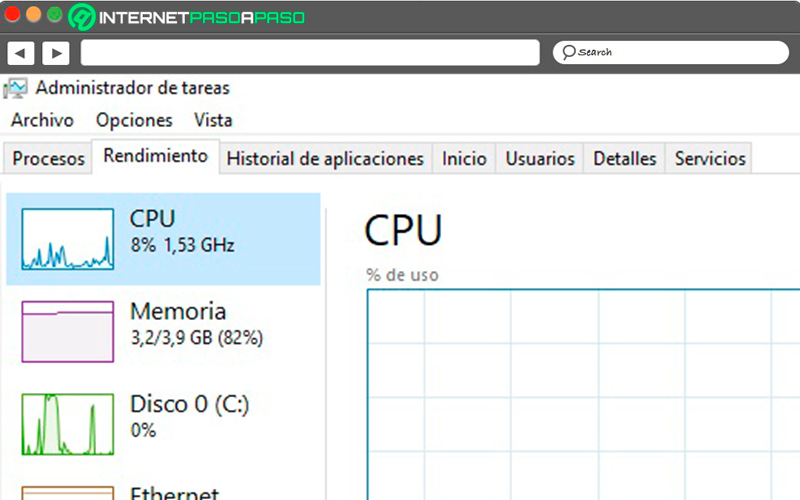
- CPUs: The most relevant data of this component observed in this tab are:
The processor model: easily observable in the upper right corner.
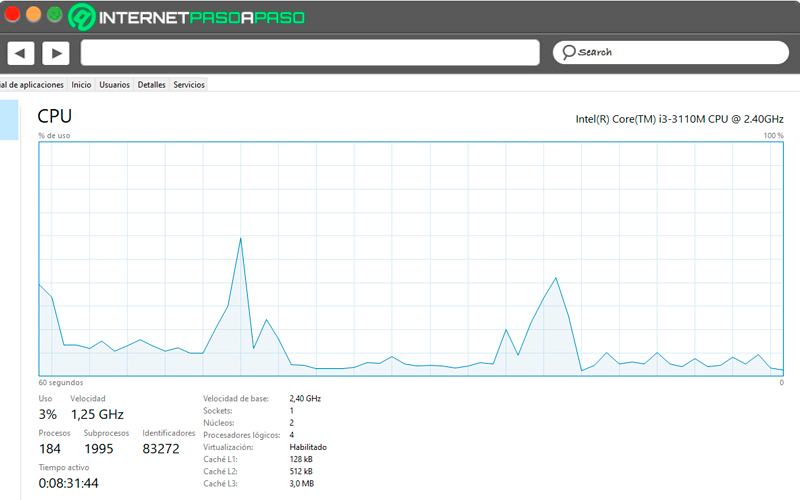
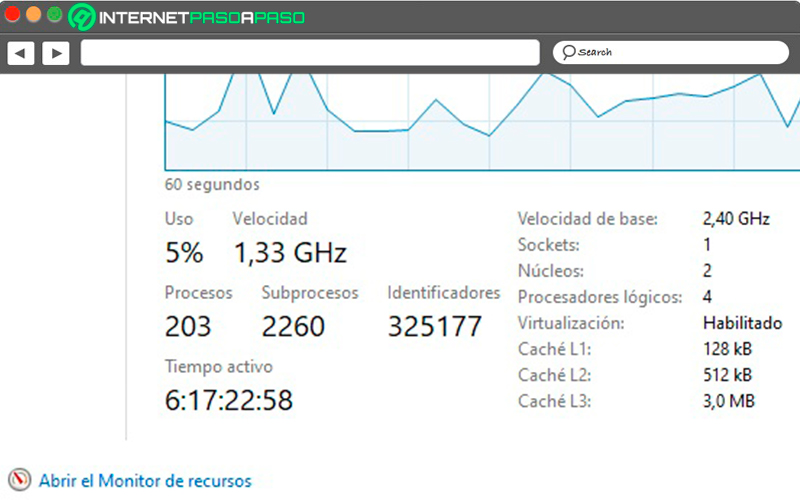
Processor capacity in use, speed in Hz and number of processes and threads that are being performed. All of this is visible at the bottom of the chart.
- Memory: In this section we can find the elemental information of our RAM:
RAM capacity and DDR generation: easily observable in the upper right corner of the performance graph.
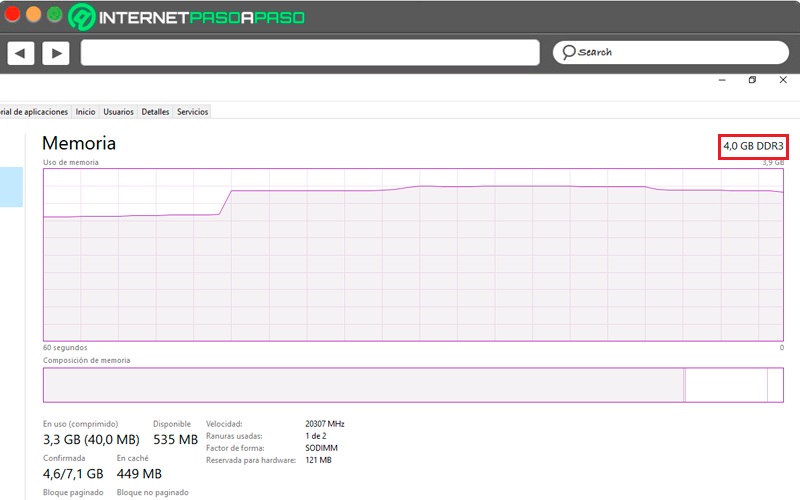
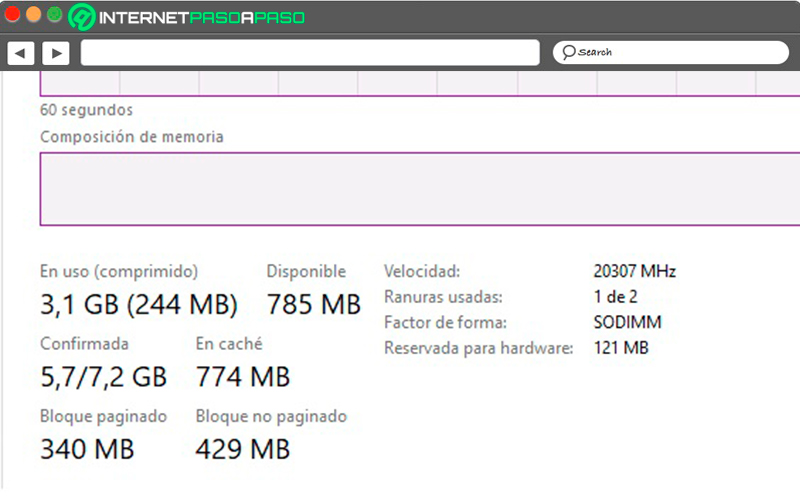
Megabyte capacity in use, remaining available capacity, and cache usage. If the latter is very high, it is recommended to clean it. It is displayed below the graph.
- HDD: In the section of the disc we find the performance of this at the moment in its respective graph. As well as other important information:
Hard drive name and model: easily visible in the upper right corner of the screen.
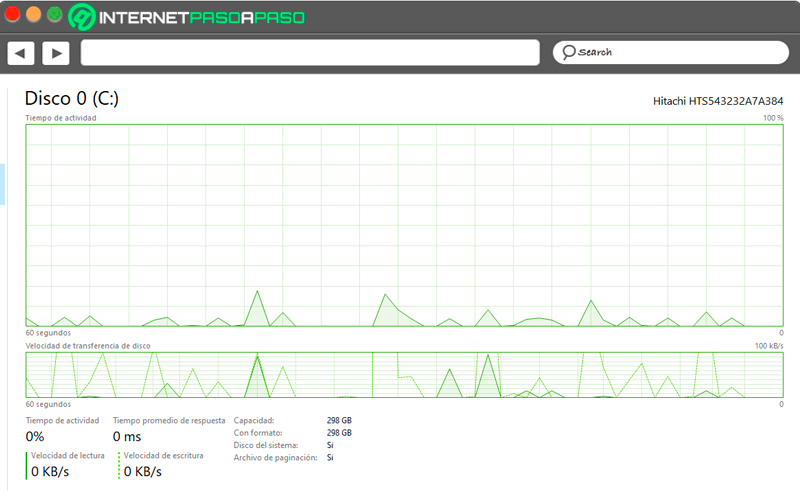
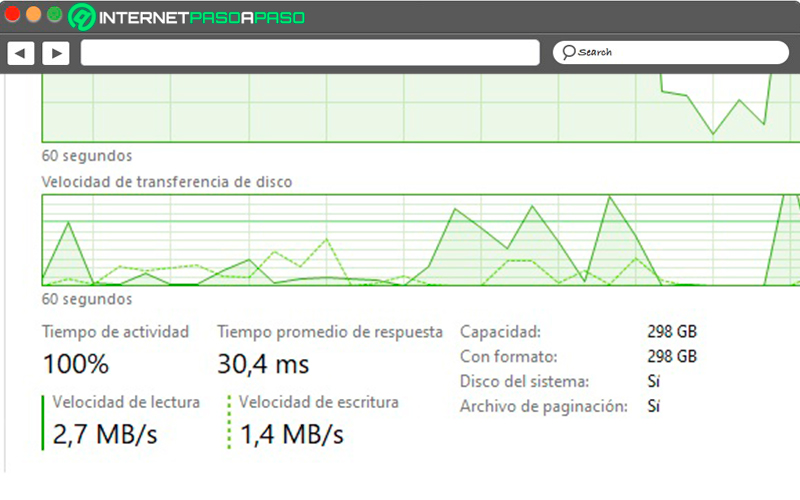
Read and write speed measured in MBps and net hard drive capacity. It’s in the bottom left of the screen.
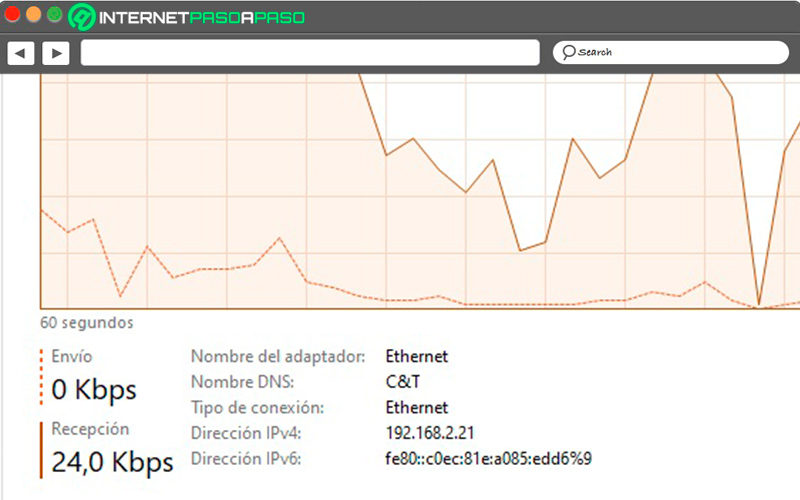
- Net: The last one will be tentative to the Internet connection model that is being used, being “Ethernet” if it is by cable and “Wifi” if it is wireless. Therefore, we will be able to see the metrics of the controllers that are active. If there is no Internet connection, nothing will be displayed.
Network controller name and model: We find it in the upper right corner of the screen.
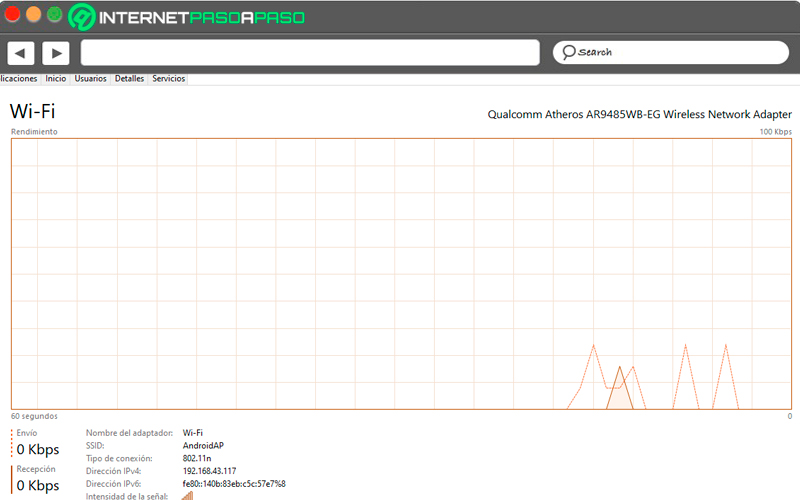
Naturally below the graph we will find the Kilobits sent and received per second, as well as the main source of the connection.
app history
This tab shows the history of all programs that qualify as an application in our system and the consumption generated during its use throughout the day.
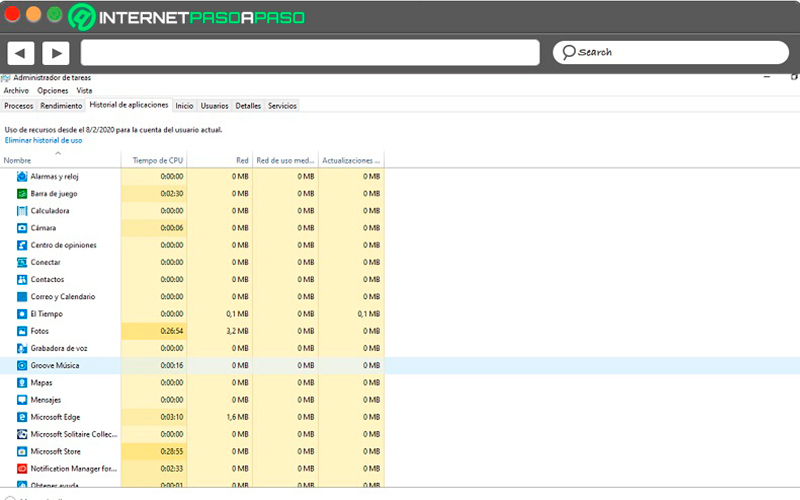
Application should be understood as all those programs that are installed by default on the system.
Start task manager
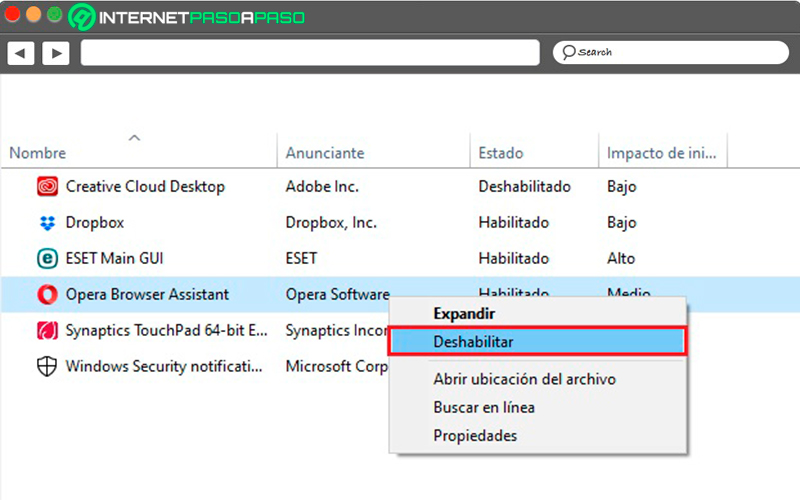
In this section we will find all the program services that open when the system starts. Namely, those that just turn on the computer are activated.
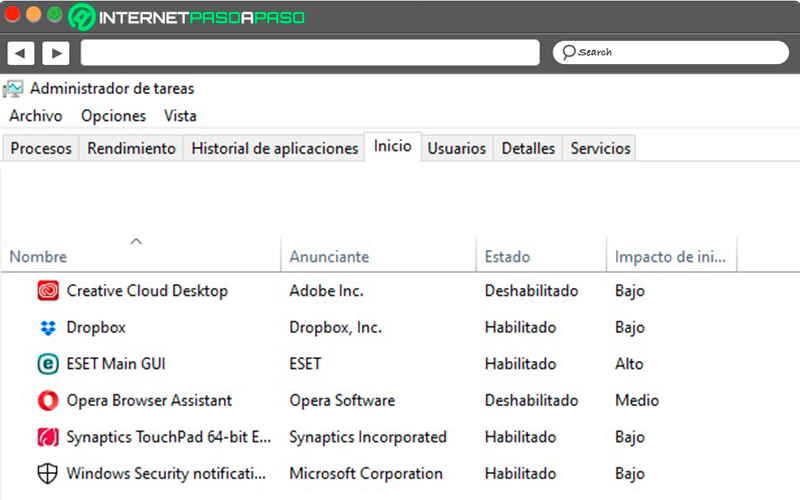
From here we can deactivate them if we notice that they are having a negative impact on the startup speed of the computer. To deactivate them we must right-click on the service and select the “Disable” option.
Users
From here it is possible to monitor all the movements of the computer users in case there are different active sessions. You can also view the metrics of the general consumption of each of the sessions.
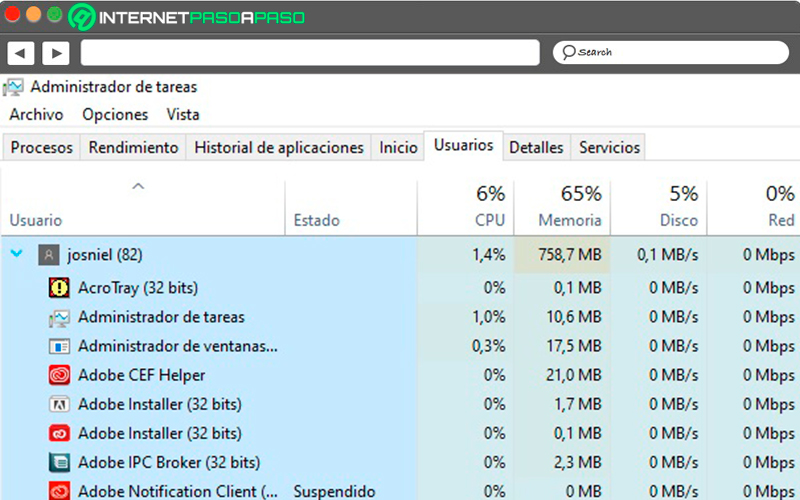
This also serves to detect any program that is slowing down the computer and close it.
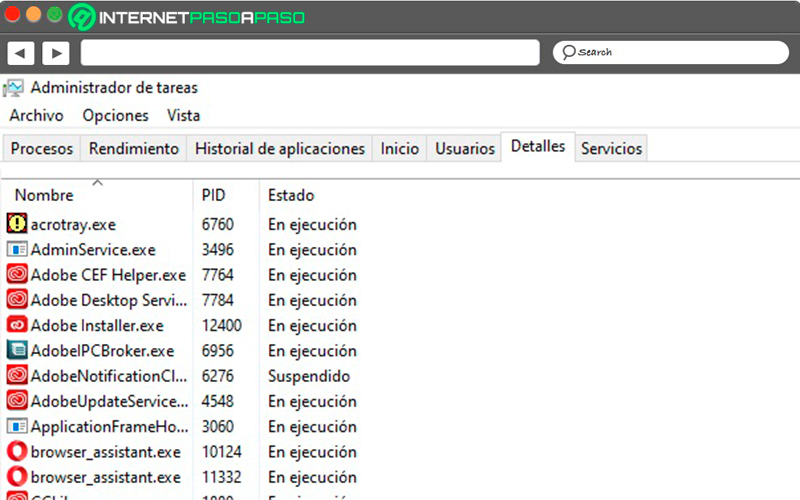
Details
In it you can see all each of the processes carried out by each program. It is designed so that experts in the area can suspend or run any of them.
Services
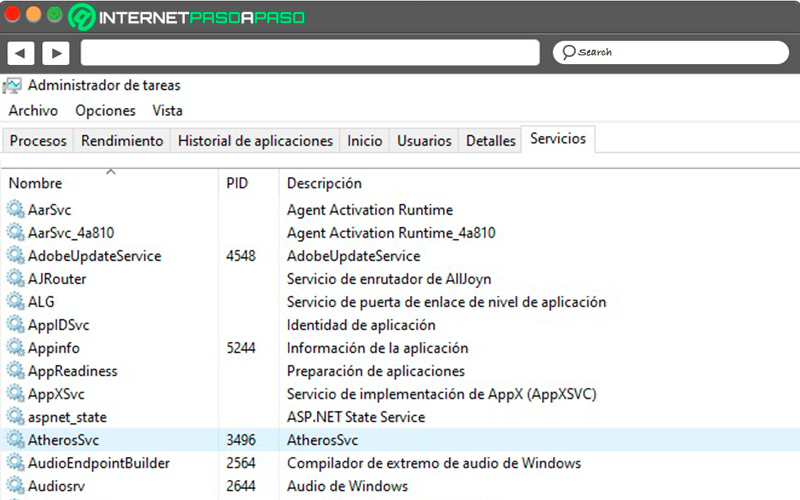
In the last tab we clearly find all the Windows services and each of the components of the computer. So it is only recommended activate or deactivate under the supervision or advice of an expert.
Steps to open and use task manager in Windows 10, 7 and 8:
Windows is unique in that it makes accessing the Task Manager as easy and fast as possible. Let’s see how to do it in the currently most popular versions.
on W10
In Windows 10, all you have to do is right-click on the taskbar at the bottom of the screen and then choose the option “Task Manager”.
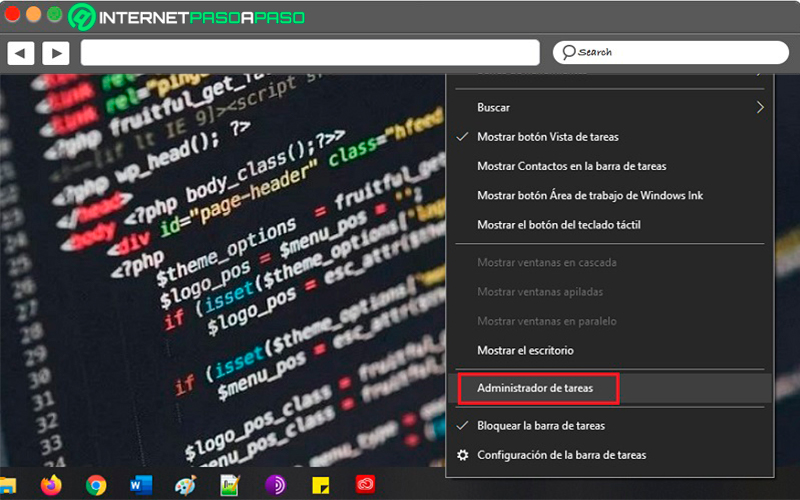
On Windows 8
The Windows 8 system interface is similar to that of Windows 10, so the above procedure is totally valid. But, it is also possible to do it by pressing the keys “Ctrl+Alt+Delete”. This enables us a menu where you can choose the option “Task Manager” easily.
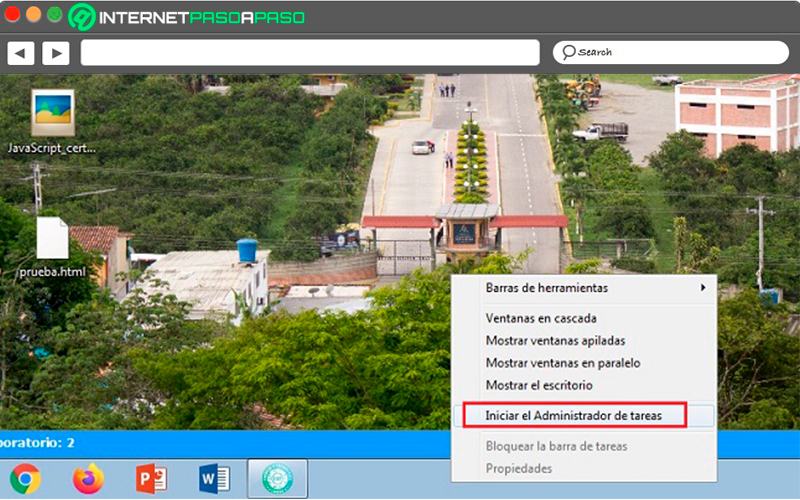
on Windows 7
Finally, in Windows 7 it is the same way, but since the interface is different, here we show you exactly how to do it. Right-click on the lower taskbar and then choose the option “Start Task Manager.”
Tricks that you probably did not know about the Windows task manager
- If Task Manager ever hangs or stops working, you can start another one by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + ESC. “Winlogon will look for an existing instance and try to revive it for up to 10 seconds. If that Taskmgr doesn’t start making sense by responding to the secret code in that time, another one will be launched. That way you’re never without a Taskmgr as long as some resources are available.”
- Task Manager will load in reduced mode if resources are low: For example, it will only load the processes tab if that is what it needs to boot. “It’s one of the few apps that doesn’t ‘crash and go’ when things go wrong.”
- If Task Manager gets corrupted internally, kill or close it: Restart it by pressing and holding CTRL + ALT + SHIFT and Task Manager will reset all its internal settings to factory if it detects that key combination at startup.
- If all the title bars disappear and you only see one chartdouble click on the dead space of the client to switch to normal mode.
- CTRL + SHIFT + ESC will launch Task Manager without any help from the Shell. So if the shell or explorer is dead, you can use this key combination to start Taskmgr and restart the shell. Even if your taskbar is gone, this combination should work.
- If the shell can’t start something or hangs, try Task Manager: This has a mode where it will load without any reference to shell32.dll and will allow programs like CMD.EXE to be started without the start menu.
- You can find the binary to run any process in the processes tab: just right click and select “Open file location”.
- There should be nothing Task Manager can’t kill: Will escalate privileges (if you have them) and enable debugging privileges to attach and kill apps if needed. “If Task Manager can’t kill it, you have a kernel problem.” Here Plummer notes that after Windows XP some intentional limits were added to what Task Manager can kill to prevent the user from killing essential Windows components and self-inflicting a blue screen.
Operating systems