
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you want to know the origins of GNU Linux and all available versions? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and Learn Everything From Scratch ⭐
Linux was developed in 1991 by a computer science student from Helsinki, Linus Torvalds.. Linus started fiddling with the Minix operating system (Richard Tanenbaum) to explore the possibilities of the 386 microprocessor, and that’s how the Linux journey began. Later, Linus decided to write his operating system from scratch, without using Minix.
After asking the Internet community for help in dispelling his many doubts and after acrimonious discussions with Tanenbaum (also over the news), managed to publish a version of the Kernel in 1991 that could be considered usable. This version was made available to everyone, many people downloaded and tried it, and many felt that they could add something to this operating system and participated in its development. Linux was gradually improving from that year, until reaching version 2.4 of the Kernel.
Another important step in the history of linux evolution even what it is today is the appearance of distributions. Distributions are software packages that essentially contain the Kernel, the kernel applications, and the installation and maintenance methods for the operating system, as well as the applications. The first distributions to appear were Slackware and RedHatthe latter, although not totally free in all its versions, has always been a defender of Linux and has welcomed well-known figures from the Linux world into its ranks.
What is the GNU/Linux OS? Definition of Linux
Linux is mistakenly known as an operating system, when it is the system core (kernel). In fact, the correct name is GNU/Linux which has as its main advantage that it is totally free, free and open source software.
What is the GNU/Linux operating system and when did it start?

The system as a whole is basically the GNU system into which Linux was integrated. Linux is the core of the GNU systemone of the main components for GNU.
The GNU/Linux operating system (not to be confused with UNIX) is started when the GNU project is merged (designed by Richard Stallman and the Free Software Foundation), with the Linux system kernel (designed by Torvalds).
In January 1995 the FSF (Free Software Foundation, Free Software Foundation) gives the name to the operating system as GNU/Linux.
How does GNU/Linux work and what are its main features?
East operating system works differently from other similar programs on the market such as Windows and MacOS, since to carry out different tasks, changes or deletion of files it is necessary to use various commands to be able to execute said actions. Different from the previous ones that with just one click you can perform these actions more quickly.
Among its main features are:
- Multitask: Multiple processes can run at the same time.
- Multi-user: Multiple users can exist on the same machine.
- Multi platform: It works on different CPUS such as Intel.
- It has memory protection between processes.
- Load executables on demand: The system only reads from disk those parts of a program when it is used.
- Copy-on-write policy for page sharing between executables: Different processes can use the same memory area to run. When someone tries to write to that memory, the page (4Kb of memory) is copied elsewhere. This copy-on-write policy has two benefits: it increases speed and reduces memory usage.
- All source code is available including the complete kernel and all drivers, development tools, and all user programs; In addition, all of this can be distributed freely.
- TCP/IPincluding ftp, telnet, NFS, etc.
- Its status as an open source operating system makes it possible to take advantage of the constant advances in software, with programs developed by different people around the world.
- It guarantees an advanced level of security.
- Allows greater control of devices.
Advantage
There are many advantages that can be named, but among the main and most important the following can be mentioned:
- It is free and open source software: This means that it is completely free and that users with sufficient computer knowledge can make changes to the code or add other programs to improve the system, as long as they comply with the laws established for open source and free software.
- It has a high standard of security level.
- High performance and system speed.
- It has a wide range of free programs for use: This means that there is a wide variety of open source and free software available to all GNU/Linux users.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages, although they are few, it is important to know them, It should be noted that in some of them different programmers of this system are working to gradually eliminate them and thus improve the user experience, in turn allocating the system to more common people and not strictly for specialized users in the area.
Among the different disadvantages we have:
- Less intuitive: Its user interface is not the same as that of Windows which has been designed for common users. However, some GNU/Linux distributions have improved this aspect.
- Fewer drivers for peripherals.
- Many of the apps and programs are only in English.
- Support: The various distributions of GNU/Linux and the programs that are used in it do not have a company that supports them, or cannot provide ideal support in case of errors or failures.
What are the main distributions or versions of GNU/Linux and what uses do they have?
There are different versions for GNU/Linux and this is due to the uses that have been given to the operating system, as well as the versions or updates that have emerged over time.
Debian

It was designed for general use. It is a GNU/Linux distribution made by a community of developers and users who intended to create a 100% free softwarethis was called the Debian Project. This system is also considered a mother distribution, since countless distributions were born from Debian, such as Ubuntu or Mint.
Ubuntu
Born from Debian, Ubuntu was designed for general use. It is one of the most used operating systems along with Debian. It was developed and maintained by the Canonical company, it is characterized by its software compatibility and ease of use comparable to Mac OS X or Windows. It has several versions, among them: Ubuntu Desktop, Xubuntu, Lubuntu and Ubuntu Server.
fedora
It was primarily designed for workstations and servers. It is a stable and secure system, it was developed by Red Hatthe same company responsible for its maintenance, which has an international community of engineers, graphic designers and users who report bugs and test new software technologies as they are added. Its uses are mainly oriented to the development of software and servers.
OpenSUSE

Its use is mainly intended for system and service administration. Its distribution is sponsored by SUSE Linux GmbH; (independent division of The Attachmate Group), and AMD. This operating system is created to provide stability, power and to be manageable for really advanced uses, but to be very easy for the general public. That is, whether they are users with advanced knowledge or beginners.
Other totally free distributions based on GNU/Linux
There are other operating systems based on GNU/Linux that are totally free and open source free software, which seriously commit to this ideology. These same companies refrain from including non-free applications, manuals, and documentation.
They are between them:
- Dragora GNU/Linux
- Dyne:bolic
- GNU Guix
- Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre
- Parabola GNU/Linux
- PureOS (Librem)
- Trisquel GNU/Linux
- UTUTO XS GNU/Linux
What differences are there between the Windows operating system and GNU/Linux?
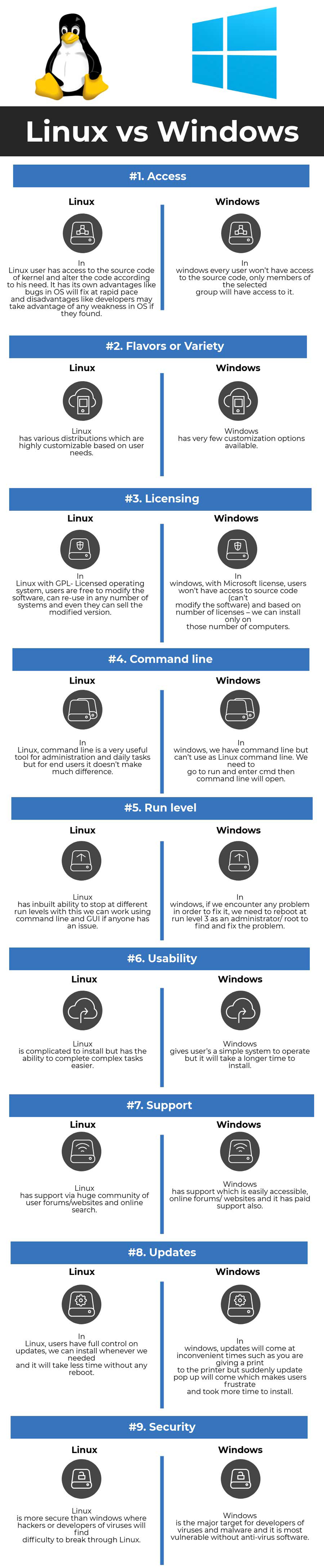
Windows and GNU/Linux are two very different operating systems. The main difference that exists is due to the free and open source software policy implemented by GNU/Linux and the private software policy used by Windows, which indicates that in order to use it, the person who acquires this system must pay to have a license and thus implement it in their personal computer.
It is also that the programs and applications available for GNU/Linux systems are totally free and in the same way they come with open source, which allows them to be modified by any user.
While in Windows, acquiring almost any program or application that is required must be paid for in advance and must not be modified for any reason, doing this without authorization can bring serious legal problems. On Windows you cannot make changes to the source code, as this is illegal and violates license agreements.
In GNU/Linux, all programs must comply with the rule of being open source, and in some cases free software, (currently there are programs that ignore the GNU initiative to be totally free programs). It is usually the OS used in the supercomputers.
What kind of license does the GNU/Linux operating system have?
This is known as: GNU General Public License, or also known by its English name of GNU General Public License, (or simply its acronym in English GNU GPL).
This is a widely used copyright license in the world of free and open source software, which and guarantees end users (individuals, organizations and companies) the freedom to use, study, share, copy and even modify the software in the way they want without legal problems.
What is Linux .DEB files and what are they used for?
These packs of .DEB files they are binary documents that contain two types of records, one of them is in charge of keeping the controlled information in storage, while the other is in charge of managing all the actual data of the program for that package.
That is to say that this Debian software packages are compressed files that are commonly used within the Linux system and its different versions. where they are primarily used to perform installations on these operating systems. Other important ones are .RPM filesthese with this format are those that are used to install programs and software for this operating system.
Operating systems