
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you need to know all the types, characteristics and functions of RAM Memory? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ And discover the best information here
RAM memory is one of the essential elements of our computer.our phone, our smart TV and all kinds of devices. It is used to temporarily store data while we do tasks, relieving the load of the storage memory.
Is it is a logical element, a softwareyes ok, purchased and used mounted on a piece of hardware which is not soldered to the motherboard but can be attached and detached.
Knowing it in detail is essential to know if we are giving it the best use and if it is the best option for our computer. So that you know it yourself and, if you wish, you can change it, we are going to tell you in detail what is this software, what types exist, how it works, how to know if it is enough for you, what problems it presents and much more.
What is the RAM memory of a computer and what is it used for?
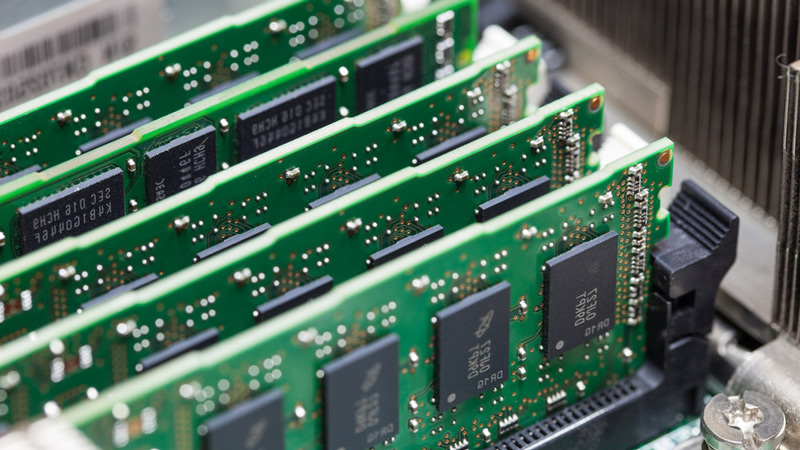

RAM is one of the three memories used by a computer. And knowing that we say computer but, in most cases, we could generalize talking about all kinds of smart devices.
The 10 best-selling RAM memories
We know that when acquire your RAM memory it is difficult to choose one, that is why we will show you below a list with the 10 best-selling RAM memories of the moment so you can choose the best one for your PC.
Best Sellers No. 1
Bestseller No. 2
Best Sellers No. 3
OFFERBestseller No. 5
Bestseller No. 6
Bestseller No. 7
Bestseller No. 8
Definition
RAM is a working memory of the logical parts of technological equipment. Better explained, we can say that it is the software that receives certain information about the tasks that are being executed in the system for, as we anticipated at the beginning, not to load the hard drive so much at the same time that we can work on it more quickly, since RAM is faster than the internal storage unit in computing.
This information is temporary, it disappears at the end of the processes, so that essential characteristic of this element is volatility. RAM memory constantly changes the information it has depending on the tasks that are being done at any given time.
In the same way, any information stored will disappear if the memory loses power. We see this clearly when the power goes out, comes back, we start and, obviously, the computer starts from scratch, it does not keep the tasks and the information that we had before the cut.
RAM is an acronym for Random Access Memory, random access memory if we translate it into Spanish. The definition of this name tells us that reading and writing are performed in any memory location, all of these being equal in terms of waiting timewhich means that the information goes to a random place as there are no more or less advantageous conditions.
Evolution
RAM replaces delay lines and relays as systems to function as memory. Is begins as a magnetic core, developed in the middle of the last century. This model, also known as bull memory, was used in computers for more than two decades.
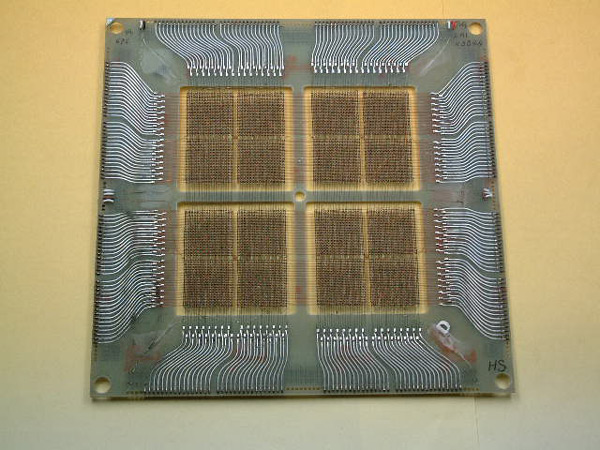
One of his requirements was storage of one byte per toroid tiny ferromagnetic, which required an amount of space that increased as more capacity was needed memory Imagine, for a few millimeters that were needed per byte, if we multiply… That became nonsense after a few years!
It is in the year 1969 when 3101 is released, a 64-bit chip that is the first RAM with a silicon semiconductor base. Intel does it, Only one year later presented what was the first DRAM memory, 1024 bytesa milestone for the success of its commercialization and, with it, the point at which the previous ones began to disappear.
The 1973 stands out in this sector for introducing what quickly became a standard and helped to reduce the size of the pieces to a great extent: the transmission of various signals (in this case, memory addresses) for a single medium. The novelty came from the hand of MOSTEK, with MK4096, 4096 bytes on 16 pins.
After its standardization, this type of memories with the aforementioned addressing scheme was directly attached to the motherboards by soldering or they were installed in sockets, occupying an important part of the printed circuit.
Its installation in the main soon evidenced the impossibility of miniaturizationso in the minds of technicians soon the memories to modules appearedwith the first being SIPP and quickly moving on to SIMM, a pinless upgrade.
Ending the 80’s the evolution of the rest of the equipment’s hardware made that the MOSTEK model was totally insufficienthaving to work hard on addressing.
The models that stood out in this aspect are:
- FPM RAM or Fast PageMode RAM: The addressing mode included that the address sending was given in a unique way by the controller, launching one after another without having to generate the total number of addresses at the same time. Access times were 60 and 70 nanoseconds, which was a significant time saving.
- ODE RAM or Extended Data Output RAM: Access times were reduced to 30 or 40 nanoseconds, sending contiguous addresses while addressing the column to use and reading the previous one, eliminating the wait state and making the buffer always active in each cycle
- BEDO RAM or Burst Extended Data Output RAM: It made use of internal address generators, accessing various memory locations per clock cycle, increasing the benefits of its predecessor by 50%.
Functions on PC and mobile devices
In any device, the use of RAM memory is always the same, the one already mentioned: store data of tasks that are being executed at the moment, so that they have quick access to them and that they can also be easily deletedquickly leaving room for information from any other task to fit in.
Types and examples of RAM or random access memory

There are two types of RAM: SRAM and DRAM.. Within these, we see that they can be classified according to different factors or elements. Let’s see a first general scheme and then we will explain the most significant details of each type.
-
SRAM:
- volatile.
-
Not volatile.
- NVRAM,
- MRAM.
-
DRAMS:
-
asynchronous DRAM. We have already seen these before, as an important part of evolution.
- FPMRAM.
- EDO RAM.
- BEDO RAM.
-
SDRAM.
-
RAMBUS
- RDRAM.
- XDR DRAM.
- XDR2DRAM.
- SDRSDRAM.
- DDRSDRAM.
- DDR2SDRAM.
- DDR3SDRAM.
- DDR4SDRAM.
-
RAMBUS
-
asynchronous DRAM. We have already seen these before, as an important part of evolution.
SRAM or Static Random Access Memory
Semiconductor based technology that kept memorized data while it was connected to the current without having to use the refresh circuits, as had been happening with DRAM memories.
Compared to its competitor, consumes less, is faster and more expensive. For this reason, its use is given to carry out activities with a high demand for time or consumption. They can be volatile or non-volatile, synchronous and have a bipolar junction transistor or MOSFET for CMOS.
NVRAM or Non-Volatile Random Access Memory
It is a non-volatile SRAM memoryis that you will not lose the information after disconnecting from power. This makes it a bit far from its own definition, but it is a fairly specific type used in routers and computers, not computers.
For this reason, they are a kind of predecessor of reprogrammable ROM memoriesbecause they maintain, like these, a minimum information necessary for the launch of the devices.
MRAM or Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory
It also happens to be a non-volatile SRAM memory that was developed in the 90s but that, due to the generalization of DRAM and flash memory, was not consumed too much, falling into oblivion despite having defenders who indicate that it will end up being imposed.
Works by storing data by magnetic force and not as an electrical charge. It includes two ferromagnetic disks that maintain a magnetic field each. They do not require a drink and do not consume energy continuously. Also, its accesses are around 2 nanoseconds.
DRAM or Dynamic Random Access Memory
this memory is based on capacitors and it is characterized by progressively hanging the load, so that a refresh circuit must review it and replace it through refresh cycles. Very long-lived, since the 1960s, and of current use for most main memories in computers and other devices.
asynchronous DRAM
The subtypes of the previous scheme already we have seen them in the evolution section.
RDRAM or Rambus Dynamic Random-Access Memory
In his time he was fastest synchronous DRAM memoryalso famous for working in a different way, giving us a large bandwidth, but also seeking to solve the problems with the number of pins and with the granularity.
This means that, clearly, it was not an economic element, which is why it soon had a substitute. His presentation was made in RIMM modules with 184 contacts. It began to be used in the well-known Nintendo 64 console, in the Pentium 4 and in other later devices.
The following types were available:
- PC600: Working at a maximum of 300 MHz.
- PC700: Operating up to 350 MHz.
- PC800: It could work up to 400 MHz.
- PC1066: It would reach 533 MHz.
- PC1200: Its maximum performance was supposed to reach 600 MHz.
XDR DRAM or Extreme Data Rate Dynamic Random Access Memory
Other Rambus SDRAM memory, or rather a high performance implementation that succeeded the previous Rambus. Remarkable for eliminating latency and for having a maximum capacity of 1 GB.
Its use is perfect in small systems that require high performance, such as the Play Station 3 console, and high-performance GPUs. It had a very similar second version but that improved, of course, some aspects. This happened without pain or glory due to the imposition of other memories of the competition.
SDR SDRAM or Single Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory
Is a synchronous memory dating from the 70s whose access times fluctuate between 10 and 25 nanoseconds.
His presentation is given in DIMM-type modules that have 168 contacts and the data buses were 4, 8 and 16 bits. Its use occurred in the second and third generation of Pentium processors as well as in several AMD.
The types offered of this type of RAM are:
- PC66: It will work at 66.6 MHz maximum.
- PC100: Operation occurs at a maximum of 100 MHz.
- PC133: at 133.3 MHz maximum.
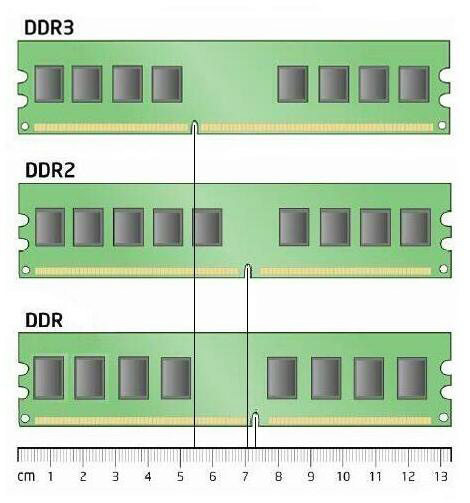
DDR SDRAM or Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory
A synchronous memory that will send two data groups in each clock cycle, hence its name. That is, it is twice as fast without having to increase the clock frequency.
Featured in DIMM modules with 184 contacts for use on desktop computer and 144 contacts if we opt for those that are integrated into laptops.
The types that exist are:
- PC1600: Maximum use at 200 MHz.
- PC2100: Maximum performance at 266.6 MHz.
- PC2700: It offered a frequency of up to 333.3 MHz.
- PC3200: It reached 400 MHz.
- PC3500: It could reach 433 MHz.
- PC4500: It could work up to 500 MHz.
DDR2SDRAM
It is simply an enhancement of the previous type where the input and output buffers can run at double core frequency to do four transfers per clock cycle. His presentation will be in DIMM-type modules with 240 contacts.
The types we found are:
- PC2-3200: Works up to 400 MHz.
- PC2-4200: Its operation occurs up to 533.3 MHz.
- PC2-5300: Will work up to 500 MHz.
- PC2-6400: Work will be performed up to 800 MHz.
- PC2-8600: Work is done up to 1066.6 MHz.
- PC2-9000: The maximum MHz that can be reached is 1200.
DDR3SDRAM
Improving the previous ones, they stand out for their high performance under low voltage conditions, making consumption lower overall. They are presented in 240-pin DIMMs.
Its types are:
- PC3-6400: The maximum frequency may be 800 MHz,
- PC3-8500: Its maximum frequency would reach 1066.6 MHz.
- PC3-10600: The maximum work will be 1333.3 MHz.
- PC3-12800: Its maximum operation includes a frequency of 1600 MHz.
- PC3-14900: Clock work will be given at 1866.6 MHz.
- PC3-17000: Will work up to 2133.3 MHz.
- PC3-19200: Its maximum work can be developed at 2400 MHz.
- PC3-21300: The maximum frequency is 266.6 MHz.
DDR4SDRAM
consume less than the previous ones and yield more. Otherwise, your work is done the same way. They are presented in 288-pin DIMMs.
The existing types so far are:
- PC4-1600: It has a frequency of, at most, 1600 MHz.
- PC4-1866 : The frequency it will reach is 1866.6 MHz.
- PC4-17000: 2133.3 MHz maximum for its clock frequency.
- PC4-19200: Its work is done up to 2400 MHz frequency.
- PC4-25600: Reaches a very high frequency of 2666.6 MHz.
Types of modules or slots of RAM memory
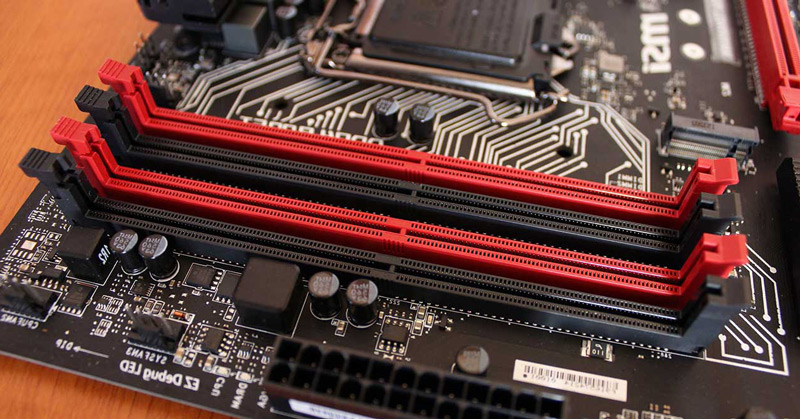
A module of a RAM It is a printed circuit board to which DRAM chips are soldered on one or both sides.. With that a high memory density is achieved in relation to the number of transistors used.
These also include an integrated, which will allow the identification of the modules by the team using the SDP protocol. As was the case with the most basic design of random access memory, an evolution was becoming necessary that would allow the exchange of modules and compatibility between manufacturers.
Thus, the following types of slots emerged:
- dip package either Dual Inline Package.
- SIPP package either Single In-Line Pin Package. First commercial memory module; with proprietary format.
- RIMM modules either Rambus Inline Memory Module. Well known and released by RAMBUS.
- SIMM modules either Single Inline Memory Module. With data bus in 16 or 32 bits. For old computers.
- DIMM modules either Dual Inline Memory Module. With 64-bit data bus. For current desktop computer.
- SO-DIMM modules either Small Outline DIMM. For laptops; It is nothing more than the mini version of the previous one.
- FB-DIMM modules either Fully-Buffered Dual Inline Memory Module. For servers.
How to know how much RAM memory I have installed in my computer and if it is enough?
Although this information is always found in the system information folders, access to these depends not only on the operating system that we have installed but also on its version. Let’s look at the most general examples, Windows 10 and Mac.
Windows
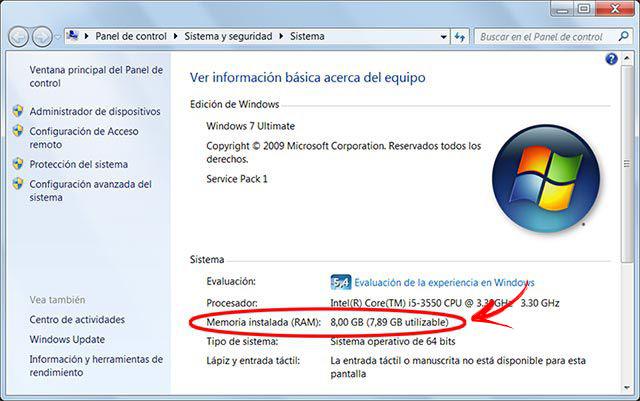
As simple as:
- Go to home bar (by clicking on its icon at the bottom left on our desktop or by pressing the keyboard button with the corresponding access).
- Type in the search box “RAM“.
- One of the results will be “View RAM information“, next to an exclamation mark icon. Click on it. You will directly access the Control Panel area where you can see this information. You will see that it says “Installed RAM“, followed by a gross amount and, in parentheses, the net amount that you can use.
You can too:
- Anger Start.
- Click on the “Setting“, which is on the left and is the gear.
- In the new window, click on the house icon, “Start“.
- Now about the option of “System“, with the computer.
- On the left row of tabs, scroll down to “About” and press it. The window that appears already shows you the information you are looking for.
Another option is:
- also go to Start Menu.
- Introduce “System” in the search box.
- Among the results, click on the “System” option (includes an icon of a computer). This opens the screen with system information, including the amount of RAM you have installed.
Mac
In this case you must:
- Click on it apple iconin the bar, top left.
- Click on “About this Mac“.
- A small information window will open. Click on “system report“.
- Another window full of tabs will open in the area on the left. Now hit “Memory“. Here you will know the existing slots in your computer, the ones that are in use, the memory size of each module, the type of RAM and its speed.
Knowing if it is enough is as simple as checking how much is usually used. If performing the basic tasks of each day is working at high percentages, you should consider expanding it or changing it for another of a more current generation.
To check this:
on Windows
- At any time, press the buttons “Ctrl”+”Alt”+”Delete” at the same time.
- A screen will open with several options, one of them being “Task Manager”. Press this.
- When you do, you will see that a window opens in which you can see the performance of certain parts of the system in relation to the processes that are open.
- You have to pay attention to the percentage displayed above the word memory; this is the amount of RAM that the system needs to do what you are doing at the moment. If the percentage is high and you consider that you are doing very little, it is because the memory is clearly insufficient..
- As a curiosity, if you click on the arrow next to the percentage, the processes will be ordered according to how they consume more memory, from more to less. This can be useful to check if there are processes open that shouldn’t be, or to see if any can be replaced by a lower power option.
on Mac
- Go to the folder of “Applications/Utilities“.
- Click on “activity tracker“.
- From the available tabs, click on “Memory“. Here you will find a lot of information, but the basic one is the traffic light (green for “everything is ok”, orange for “there are processes that slow down your computer and consume too much” and red for “alert, something is wrong”, basically).
What characteristics should I take into account before buying and expanding the RAM of my PC?
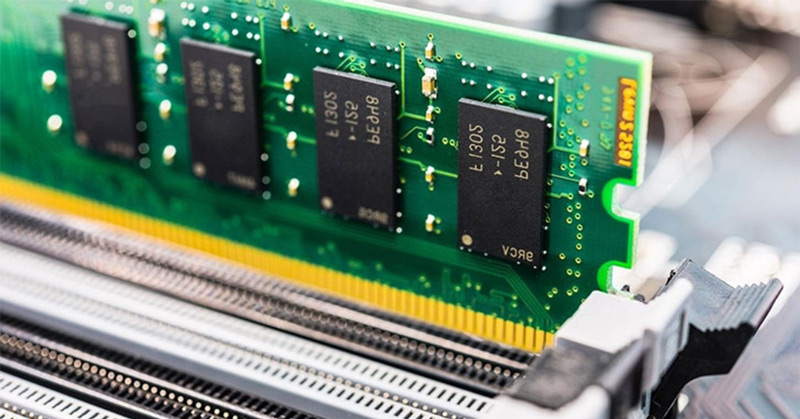
In general, this is one of those cases in which we can say that the more sugar, the sweeter, being logical that The higher the capacity and the higher the characteristics that we have been seeing, the better product and more suitable for any equipment..
That is the basis, but, of course, there are some exceptions. We must also consider that taking this into account, the budget would skyrocket and there would be no limit, every two times three we would be expanding RAM.
-
Number of slots: Attention because this is essential.
- If you only have one slot for RAM, you will have to buy as many GB as you want to finally haveso your current one cannot be used.
- If you have two slots you can buy another memory module same as yours and plug it into the remaining slot, doubling the memory. Another option is to buy two equal modules of greater capacity.
- With three or more slots (it is not usual but there are computers that have them), there is no problem, you can add identical modules to yours if you consider that its characteristics are adequate and that you simply need to multiply the amount of GB.
- Current memory type: It is possible that your computer does not work well because the type of memory is not the most suitable. Perhaps the amount of GB would be enough if the type was more current. You have to consider the type and the frequency at which your module works. Think that if you are going to add another one, it must have the same characteristics and if these are not effective, no matter how much memory you integrate, you will not solve your problem.
- Adaptation with the rest of the components: Of course, you also have to consider the rest of the elements that make up the team. It’s not going to do you any good to put more and more memory if it works in conjunction with elements of older generations, because, as much as RAM is great, the rest will act as a bottleneck, so that you can never use all that your new memory has to offer. There must be a balance; if you are improving the RAM and the rest is not, there will come a time when there is an obvious imbalance that will not be solved with more GB.
Solution and most common errors of RAM memory
Errors related to RAM memories are classified into Soft Errors and Hard Fails, depending on its origin. Let’s see what they consist of and how they are generally solved.
soft errors
This is the name given to those errors that occur in the logical part of the memory. Are the sign of having incorrect data and they generally mean that some stored information is lost, although this is not always the case, far from it. The cause of these is presence of radioactive elements in the electronic package.
Detection is done in two ways:
- parity bits: It is done the save one additional bit for each byte of data that the module has, so that you can do a reading and see if the number is odd or not. This will mean that know the parity of operation of that memory.
- ECC: spot the mistakes parsing groups of up to 4 bits; the fix is applied if a single bit is affected.
Hard Fails
Indicate that there is a hardware fault. Its detection is simple, since it is a physical problem. You should disassemble the computer, undock the memory module and visually check what happens to it (scratches, bent pins, etc).
In general, if the problems they pose are serious and/or persistent, you will have to replace it and refresh RAM, simply because its repair, unless you know how to do it yourself, is very expensive due to how delicate it is. Other times there is no solution.
Symptoms of errors in RAM
Some surprises that we can take and that indicate, with almost total certainty, that your random memory is failing are the following:
- Low performance in circumstances in which it did not occur before.
- Insufficient memory message.
- Shaky hard drive light.
- Blue screen.
- Failure to load the operating system.
- Computer not restarting.
- constant reboots.
- Beeps during power up.
- Monitor no response.
RAM error fix
To try to solve the errors that may be occurring:
- Clean your computer oftenwith special interest in connections.
- Take a look at the RAM modules; they may have moved due to vibration. You will have to fit them perfectly into their sockets.
- If the module has broken plastic parts, stick them and file them so that they remain with a structure similar to the original.
- Use a voltage stabilizer to balance the voltage received by the computer.
Main differences between RAM and ROM
Although both concepts could be confused both because of the similarity of their acronyms and because they are two types of memory, the truth is that they have little or nothing else in common. see all differences between ROM and RAM here.
RAM
We have already seen what this element consists of:
- Any byte is accessed without doing its precedents.
- Turns out to be volatile, modifiable, automatically, depending on the tasks what we do It’s faster. Your effort is temporary.
- Works with retrofitted optional software not related to operation of the team.
ROM
- A ROM memory read only. Read to boot the computer due to the impossibility of accessing other types of memories before the start.
- Memory information is essentialincluding data on system configuration, maintenance and startup.
Hardware









