
Index:
UPDATED ✅ Do you want to know what the Arduino rotary motors are and how to use them well? ⭐ ENTER HERE ⭐ and Learn Everything From Scratch!
Currently, Arduino is considered one of the best open source electronics creation platforms that exists all over the world. Which offers both free software and hardware, offers great power, is versatile and reveals remarkable ease of use. Therefore, it is one of the most fundamental elements for the development of projects based on the DIY culture and the maker environment.
In this way, this platform allows both creators and developers as well as fans to create any project, no matter its level of difficulty and thus, provides optimum performance with the aim of implement greater use of technology and the Internet of Things. Therefore, its expansion is disproportionate.
Now, luckily, arduino boards support a myriad of plugins with which it is possible build the different desired projects. reason why, allow to make use of rotary or rotary motors in order to program them from scratch. That is why, below, we teach you What are these elements about and how to use them in conjunction with Arduino.
What is a rotary motor and what kind of Arduino projects are they used for?
While true, the rotary engine is estimated as one of the first types of internal combustion engines that existed. Therefore, it was widely used before the First World War, in the first cars and motorcycles, as well as to propel airplanes. Whereas they are generally distinguished by operating with a crankshaft that remains fixed and thus, the engine rotates around it.
Now, basically, a rotary engine consists of an internal combustion engine that is capable of performing the four strokes of suction, compression, expansion and exhaustsimultaneously while the working chamber modifies its volume and the moving parts rotate in the same direction.
So, in essence, it works like an Otto cycle engine which, instead of having a cylinder block with a rotating crankshaft, it remains fixed and the entire cylinder block rotates around it. On the other hand, in Arduino projects, rotary motors have different uses which, especially, are dedicated to the field of home automation to automate a home, as well as in the world of electronics.
Well, usually such motors are present in any part of a home, since they are essential for the operation of fans, household appliances, personal computers, electric shavers, remote-controlled cars, etc. They can even be used for create large projects where electricity is the protagonist.
What should I keep in mind when programming using rotary motors on Arduino?

Fortunately, making use of rotary motors in Arduino reveals remarkable advantages that users should be aware of. So, here we mention the most important of them: Its components are internally balanced with rotating counterweights that favor a smoother power delivery and does not generate many vibrations.
Also, has fewer moving parts than a conventional motor and therefore, its total weight is much more optimal. On the other hand, to compile a rotary motor in Arduino, It is essential to take into account several aspects.
One of them consists of the types that can be used in a project with Arduino boards and, therefore, it is worth detailing them as follows:
- DC motors: They are also called “DC motors” and are one of the most common actuators of all. which have a function based on the alignment of two magnetic fields and its main advantage is that it guarantees effective synchronization, regardless of speed.
- brushless motors: They refer to a variation of DC motors that differs from brushes as a current rectification system. So that, turn to electronics to be able to make the commutation of the magnetic field. Thus, they are widely used in fans, ship propellers, quadcopters and other aerial vehicles that require high speed of rotation.
- Geared-down motors: They are those direct current motors that add an internal reducer to increase the torque of the motor and decrease its speed. In this way, they are commonly used to be able to drive wheels of vehicles and robotsTherefore, they are indicated for Arduino robotics projects.
- stepper motors: They are characterized by having an axis that is responsible for turning at a fixed angle called “step” when this is adjusted by a processor. Therefore, necessarily, a rotary engine of this class needs a processor to work properly. Thanks to their capacity, they are widely used in robotics. Assessing that, there are unipolar and bipolar motors within this classification.
- Servo motors: Without a doubt, it is the most used type of rotary motor to build projects with Arduino. Which, basically, provides a pulsed signal generated by a processor that transmits the desired position so that, autonomously, the servo can be located in that position. Thanks to this, are used in robotics projects (such as: robotic arms, bipedal robots, hexapods, etc.) and even allow sensors or a laser to be positioned.
- Continuous rotation servo motors: As their name indicates, they are motors that show the ability to turn around completely and thus behave as a DC motor with integrated speed control. Therefore, they refer to a variant of a conventional servo motor, only the electronics are modified so that the signal controls the speed (and not the position).
Now, another aspect to consider when programming these elements in Arduino, outlines the necessary requirements to consider a practical rotary engine.
Therefore, here we inform you of these requirements so that you can verify them when you want to acquire one of them:
- Seals for working chamber gas have to be three-dimensionally reliable. This means that the motor in question must be constituted from the connection of individual seals in a three-dimensional manner.
- Every moving part must make a rotary motion including the timing mechanism. Reason why, the structures that need valves and suction and/or exhaust mechanisms using oscillating motion rotors are not appropriate.
- All construction parts need resistance to fatigue at high speeds and pressures. This means that they must have sufficient capacity, in size and shape, to withstand high pressures, heat loads and sliding speeds.
- They have to carry out a relevant exchange of gases in the suction and in the exhaust.. It is essential that the engine provides enough time for suction and exhaust, especially when there are high revolutions and speeds.
- Sufficient lubrication and cooling must be provided. Which requires high durability, high heat loads and high sliding speeds. In this way, comply with sufficient capacity to withstand these factors.
Learn step by step how to program a rotary motor in Arduino from scratch
First of all, the connections will depend on the type of rotary motor you want to use with the Arduino. Taking into account that, they should all have three wires (one that will go to ground, one for the 5 volt supply, and a third wire for a PWM pin). Thus, after carrying out the connection, it is possible start the process of programming a rotary motor in the Arduino IDE from scratch which, when building a certain project, is the most interesting of all.
In this case, the steps to follow are the following:
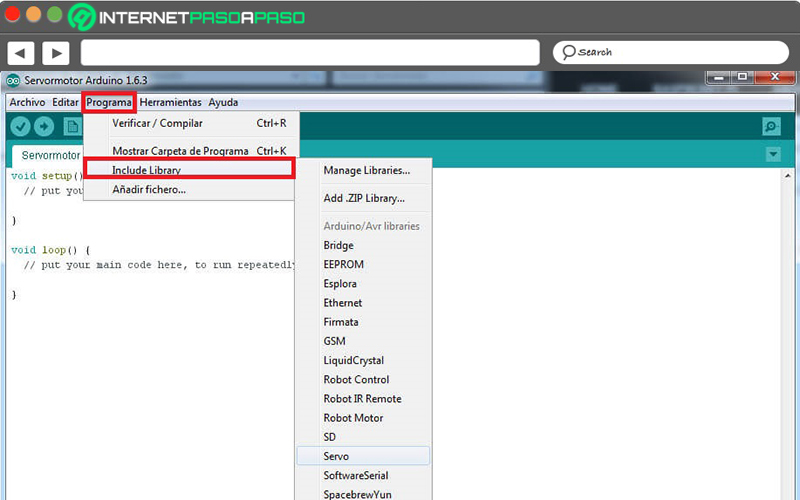
- First of all, it is necessary that make use of an external library to help you control the type of rotary motor you are using. In order to do so, proceed to incorporate said library in the Arduino environment through the tab that says “Program” on top.
- Once you select that tab, click on the option that says “Include Library” and in this way, a menu will be displayed from where you have to choose the engine used (for example, “servo”).
- Done the above, you will have already done an “include” in your programming code which allows you to control the motor in question. In addition, you can make use of a basic code (explained later) to position it at angles from 0° to 180° (ie: 0°, 90° and 180°).
- Basically, in that code, it’s useful to declare an object or variable through the “Servo.h” library, for instance. Taking into account that this process admits two methods: (1) “attach” to set which pin you have connected to your servo. (two) “write” to indicate the angle at which the rotary motor will be positioned.
- That way you can control your motor in Arduino in a very simple waythanks to the use of the library “Servo.h” in this case.
Here is the simple code to rotate the motor from 0º to 180º:
// Incluímos la librería para poder controlar el servo
#include <Servo.h>
// Declaramos la variable para controlar el servo
Servo servoMotor;
void setup() {
// Iniciamos el monitor serie para mostrar el resultado
Serial.begin(9600);
// Iniciamos el servo para que empiece a trabajar con el pin 9
servoMotor.attach(9);
}
void loop() {
// Desplazamos a la posición 0º
servoMotor.write(0);
// Esperamos 1 segundo
delay(1000);
// Desplazamos a la posición 90º
servoMotor.write(90);
// Esperamos 1 segundo
delay(1000);
// Desplazamos a la posición 180º
servoMotor.write(180);
// Esperamos 1 segundo
delay(1000);
}
List of the best rotary motors to work with Arduino that you should know
Although, previously, we pointed out the main types of rotary motors that are suitable for working with plates Arduino and programs by means of this software; the truth is that there are certain specific models of these engines that are optimal for building quality projects.
Therefore, in this section of the post, we will detail some of the best rotary motors to use in conjunction with Arduino:
brushless brushless motors
As its name indicates, They are brushless motors. and thanks to this, they do not generate any friction when turning; as a consequence, its performance is higher. Thus, they are defined as a variation of DC motors that, with the aim of provide a high quality current rectification systemdispenses with the brushes and instead resorts to electronics to effect the commutation of the magnetic field.
In this way, the main advantages of this type of motors for Arduino is that have a high speed rangehigher performance, longer battery life, better power with less weight and size, little heat loss and minimal electronic noise. It also dissipates heat better and require less maintenance due to lack of brushes. However, it should also be noted that are more expensive and more complexThey even only work with Lipo batteries.
servo motors
Another of the most common actuators for Arduino projects, are the servo motors. Since, these can be easily implemented to build robots and everything that has to do with the robotics environment. That’s why, allow to create robotic arms, bipedal and hexapod robots, as we mentioned before. They even help position lasers and sensors, apart from the fact that they can be used in turrets. Regarding its operation, the servo motors receive a pulsed signal that is caused by a processor.
Which deals with transmitting the position you want so that the servo is able to locate itself at that point autonomously. For which, internally, it is composed of a DC motor assembled to a reducer together with a controller. A) Yes, It is characterized by offering a swivel range of 180°, since, it cannot go all the way around. But in exchange for that, Provides full control in high-precision position and rotation.
However, there are also continuous rotation servo motors in which, basically, the electronics are modified so that the signal manage to control the speed instead of the position. Thanks to that, they can make a complete turn and behave in a similar way to DC motors with integrated speed control. But these do not provide precise control over turning speed and for this, it will be necessary to calibrate the servo and adjust the signal sent, obligatorily.
Stepper motors 28BYJ-48

While it is true, stepper motors are those that have a shaft that rotates a fixed angle known as a “pitch”, once this is adjusted by a processor. Well, specifically, a 28BYJ-48 stepper motor refers to a stepper motor smaller and lower price than conventional. This, with the peculiarity that adds an internal 1/64 reducer.
Thanks to that, its overall accuracy is high, since it is less than 0.087° and a torque of 0.3 kg/cm. For this reason, it is a very useful element for precision applications (such as, for example, positioning an articulated robot, directing a sensor or a laser and rotating the platform of a 3D scanner). Apart from this, they have the ability to operate at a maximum frequency of 100 Hz and because of this, they offer a maximum speed of 1 lap every 40 seconds.
DC motors
As they are the most common motors or actuators of all, they could not be missing from this list. Which, They work based on an alignment of two magnetic fields. and, therefore, the fixed part of the motor (or the stator) has a permanent magnet that produces a magnetic field inside it. Thus, regardless of the speed and torque exerted, timing is always perfect.
Now, basically, said synchronization is due to the fact that the same angle of rotation of the motor is the one that establishes the reversal of the current. In addition to that, it is characterized by provide high turning speeds, although the control of it is not the most accurate. Among other features, we highlight that DC motors offer minimal position controldepend on the load they support and some of them integrate an encoder internally.
Computing